Rare Genetic Mutation Links Two Neurological Diseases
Globe-Spanning Collaboration Connected ‘Viking Gene’ to Dementia and ALS
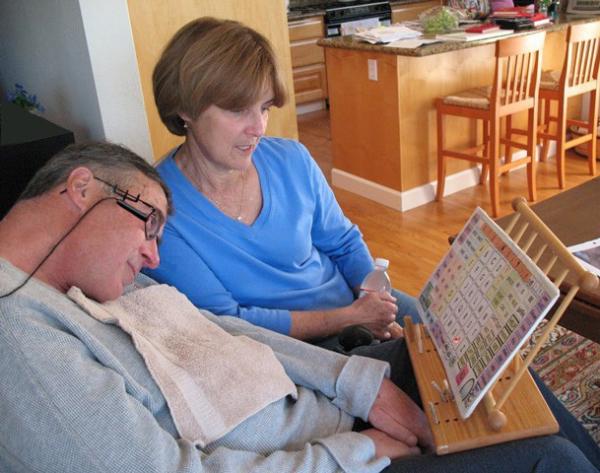
June was an important month in the life of baseball great Lou Gehrig. It was the month he was born and the month he was first picked for the Yankees’ starting lineup. Sadly, it was also the month in 1939 when he was diagnosed with the neurological disease that bears his name — Lou Gehrig’s disease, also known as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) — and the month he died of that disease two years later. It is appropriate then that ALS Awareness Day is observed on June 21 as a day of hope for those searching for effective treatments and, ultimately, a cure.
IRP senior investigator Bryan J. Traynor, M.D., Ph.D., a neurologist at the National Institute on Aging (NIA), is one of the people leading that search. Best known for his work unraveling the genetic causes of ALS and frontotemporal dementia (FTD), he led an international consortium of researchers that uncovered a mutation on chromosome 9 that is the most common ‘familial’ cause of both ALS and FTD. In fact, this mutation, which disrupts the function of the C90RF72 gene, is responsible for 40 percent of all familial cases of ALS and FTD in European and North American populations, meaning cases in which a family member also has the disease. The discovery, published in 2011, revolutionized the scientific understanding of neurodegenerative diseases and the relationships between them. It also suggested a potential target for future gene therapies.