COVID-19 Timeline at NIH (September-October 2022)
COVID-19 Research and Activities at NIH
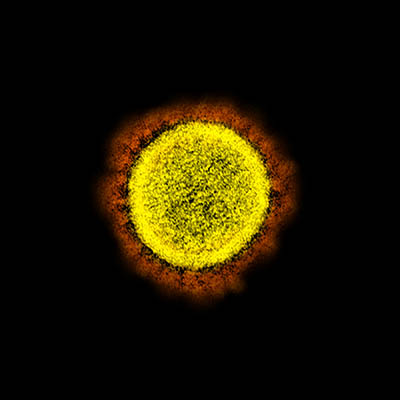
NIAID
Transmission electron micrograph of SARS-CoV-2 virus particles, isolated from a patient. Image captured and color-enhanced at the NIAID Integrated Research Facility in Fort Detrick, Maryland.
September 1: The CDC recommends a single updated booster dose of either the Moderna vaccine for individuals 18 and older or the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine for individuals 12 and older at least two months following primary or booster vaccination. The original monovalent boosters are no longer authorized for use.
September 2: The CDC updates COVID-19 community levels: Rocky Mountain Laboratories in Hamilton, Montana, moves from medium to low community level. Framingham, Massachusetts, moves from low to medium, and Detroit, Michigan, moves from high to medium. All other NIH locations remain at their current levels.
September 2: Lawrence Tabak (Performing the Duties of the NIH Director) emails staff with a coronavirus update. He calls attention to this week’s FDA authorization (August 31) of the Moderna and the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 bivalent boosters, which are designed to give better protection against circulating omicron BA.4 and BA.5 subvariants, and to the CDC recommendation (September 1) to get one of those vaccines. Tabak notes revised and streamlined content on the NIH Guidance for Staff on Coronavirus intranet site based on the latest information.
September 8: NIH’s RADx Tech program issues two new funding opportunities for diagnostic test manufacturers to develop the next generation of COVID-19 tests, with a focus on accessibility. The first is a call to develop accessible over-the-counter tests that can be used by people with disabilities, specifically blindness, low vision, fine-motor-skill difficulties, and aging-related disabilities. The second focuses on improving performance of over-the-counter and point-of-care tests as well as integrating universal design features to ensure ease of use. Products should be ready for commercialization in 12-24 months.
September 9: The CDC updates COVID-19 community levels: Rocky Mountain Laboratories in Hamilton, Montana, moves from low to medium community level. Research Triangle Park in Durham County, North Carolina, moves from high to medium, and Framingham, Massachusetts, moves from medium to low. All other NIH locations remain at their current levels.
September 12: President Joseph Biden announces his intent to appoint Renee Wegrzyn as the first director of the Advanced Research Projects Agency for Health (ARPA-H). She started as ARPA-H director on October 11, 2022.
September 15: An NIH-funded research team develops a method to evaluate how mutations in SARS-CoV-2 can affect recognition by antibodies used in rapid antigen tests. Because most rapid antigen tests detect the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein (N protein), the team directly measured how mutations to the N protein affected diagnostic antibodies’ ability to recognize their target (Cell 185:P3603-3616.e13, 2022).
September 15: NIAID Director Anthony Fauci gives a talk to the COVID-19 Scientific Interest Group outlining lessons learned from COVID-19. Watch videocast at https://videocast.nih.gov/watch=45929. Story in this issue of The NIH Catalyst starts on page 1. [give url for online]
September 16: The CDC updates COVID-19 community levels: Bayview Research Center in Baltimore, Maryland, and Rocky Mountain Laboratories in Hamilton, Montana, move from medium to low community level and Framingham, Massachusetts, moves from low to medium. All other NIH locations remain at their current levels.
September 16: Lawrence Tabak (Performing the Duties of the NIH Director) emails staff with a coronavirus update and encourages eligible employees to get the updated Moderna or the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 bivalent vaccine boosters. Additionally, effective November 1, 2022, NIH asymptomatic testing services will only be offered to staff members with direct patient contact or referred by Occupational Medical Service based on job duties required to keep the workplace safe. Tabak highlights the September 8 RadX Tech announcement about new funding opportunities for diagnostic test manufacturers to develop the next generation of COVID-19 tests.
September 21: The National Science Advisory Board for Biosecurity (NSABB) convenes virtually to discuss its progress in reviewing existing national biosecurity oversight frameworks governing research with enhanced potential pandemic pathogens and dual-use research of concern. The NSABB is a federal advisory committee chartered to provide advice, guidance, and recommendations to the United States government regarding potential biosecurity implications of life sciences research.
September 23: The CDC updates COVID-19 community levels: Rocky Mountain Laboratories in Hamilton, Montana, moves from low to medium community level and Research Triangle Park in Durham County, North Carolina, moves from medium to low. All other NIH locations remain at their current levels.
September 27: A large international study funded by NIH confirms the findings of a previous U.S. study that linked COVID-19 vaccination with an average increase in menstrual cycle length of less than one day (BMJMedicine 1:e000297, 2022; DOI:10.1136/bmjmed-2022-000297).
September 30: Lawrence Tabak (Performing the Duties of the NIH Director) emails staff with a coronavirus update, reporting a continuing trend of decreasing new case numbers, hospitalizations, and deaths. Starting in October, Tabak will send his coronavirus update email on the second Friday of each month.
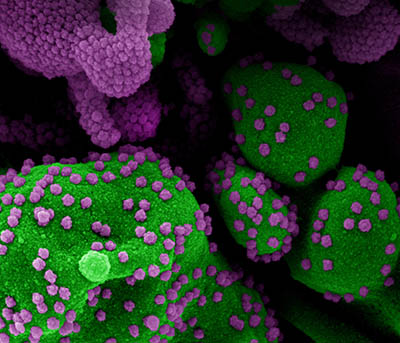
NIAID
Colorized scanning electron micrograph of an apoptotic cell (green) heavily infected with SARS-CoV-2 virus particles (purple), isolated from a patient sample. Image from the NIAID Integrated Research Facility in Fort Detrick, Maryland.
October 3: The National Library of Medicine (NLM) resumes Reading Room Operations after having been closed since March 2020 due to renovations taking place in the NLM Building as well as ongoing COVID-19 considerations. NLM welcomes customers by appointment only Monday-Friday from 8:30 a.m. to 5:00 p.m. ET.
October 6: A small NIAID-supported study of eight patients taking the antiviral Paxlovid suggests that COVID-19 rebound is likely not caused by impaired immune responses (Clin Infect Dis 2022; DOI:10.1093/cid/ciac663).
October 7: The CDC updates COVID-19 community levels: Research Triangle Park in Durham County, North Carolina, moves from low to medium community level. All other NIH locations remain at their current levels.
October 12: The FDA amends their emergency use authorizations for the Moderna and the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 bivalent vaccine boosters for use in younger age groups. The Moderna COVID-19 bivalent vaccine is authorized for administration at least two months after completion of primary or booster vaccination in children down to six years of age. The Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 bivalent vaccine is authorized for administration at least two months after completion of primary or booster vaccination in children down to five years of age.
October 14: The CDC updates COVID-19 community levels: Research Triangle Park in Durham County, North Carolina, and Rocky Mountain Laboratories in Hamilton, Montana, move from medium to low community level. All other NIH locations remain at their current levels.
October 14: Lawrence Tabak (Performing the Duties of the NIH Director) emails staff with a coronavirus update. He reports that after this week’s amended FDA authorization, the CDC now recommends the Pfizer-BioNTech bivalent vaccine booster for individuals five years of age and older and the Moderna bivalent vaccine booster for individuals six years of age and older.
This page was last updated on Wednesday, November 9, 2022
