Accelerating Therapeutic Development for Brain Illnesses
IRP Study Finds Brain Imaging Technique Could Aid Clinical Trials
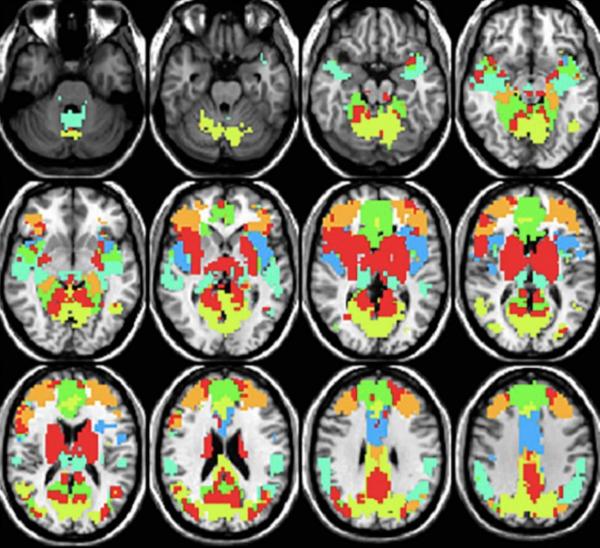
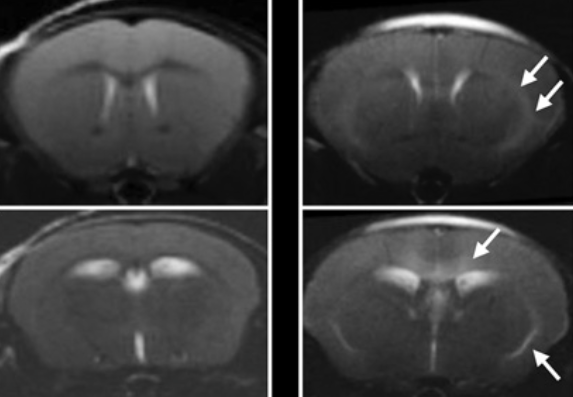
We all crave instant gratification, but unfortunately, most things worth doing take time. This certainly applies to evaluating treatments for many illnesses, as observable changes in patients’ symptoms can take weeks or months to appear. Fortunately, new NIH research has revealed that a particular way of non-invasively peering into the brain could help accelerate the development of treatments for a variety of rare neurological diseases.