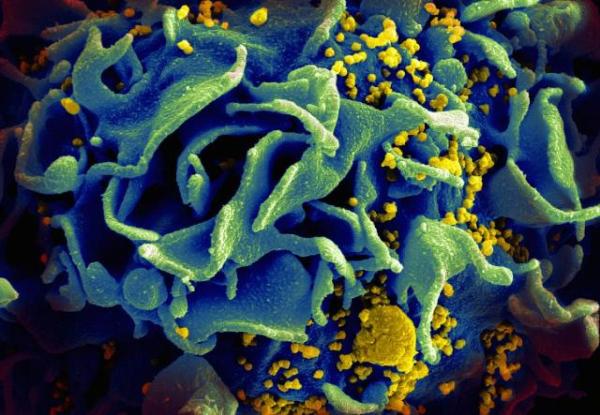
Three-Armed Antibody Could Offer Defense Against AIDS
Four Questions with Dr. John Mascola
The disease known as human immunodeficiency virus, or HIV, attacks and destroys cells vital to the immune system. This leaves the millions of people living with HIV less able to fight other infections and can lead to an extremely severe form of immune system deficiency called acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), which was responsible for nearly 770,000 deaths in 2018 alone. As of 2019, there are approximately 37.9 million people around the world living with HIV/AIDS.
Although HIV/AIDS has been recognized as a serious public health crisis, finding effective treatments, or a vaccine to prevent infection in the first place, is not a simple task. The HIV virus has many different types and strains — similar to the flu — which makes developing vaccines and treatments extremely challenging, as the virus is constantly changing. At the NIH, there are a number of ongoing collaborative research projects aimed at providing new options for those diagnosed with HIV/AIDS and those at risk for contracting the virus in the future.