Enzyme Therapy Helps Rebuild Teeth
Study in Mice Suggests a New Approach to Treating Periodontal Disease
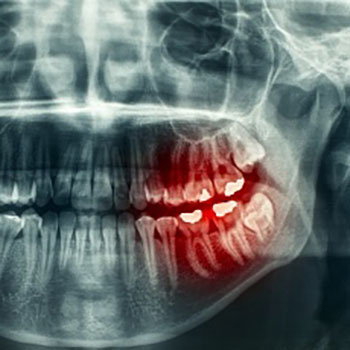
New IRP research suggests a novel strategy for treating periodontal disease, in which an infection of the gums causes the roots of the teeth to deteriorate, along with the parts of the jaw bone that support them.
Our teeth are extremely tough, but neglectful oral hygiene practices and certain genetic disorders can still massively damage them. If this deterioration becomes bad enough, teeth can be permanently lost. In a recent study, IRP researchers identified a promising new strategy for helping the body regenerate a part of the tooth that is particularly difficult to repair.1
When it comes to taking care of our teeth, the enamel coating surrounding the upper portion of teeth tends to get most of the attention. It is, after all, the most visible part of our teeth and the hardest substance in the human body. However, a substance called cementum that surrounds the roots of our teeth is also incredibly important. The cementum helps our teeth remain in our mouths by attaching them to periodontal ligaments connected to surrounding jaw bone.
“The cementum around the tooth root is one of the tissues that has to be repaired to restore the tooth’s function after periodontal disease,” explains IRP senior investigator Martha J. Somerman, D.D.S, Ph.D., the new study’s senior author. “A lot of scientists have been focusing on promoting bone regrowth, but if you do that without considering the need for a healthy cementum, you will not restore proper function.”
Unfortunately, damaged cementum doesn’t regenerate very quickly when left to its own devices, if it heals at all, and current approaches to rebuilding it have not proven to be very effective. In the new study, Dr. Somerman’s team investigated whether an enzyme naturally found in the human body called alkaline phosphatase (ALP) could help repair damaged cementum by boosting the process that builds teeth and bone, known as mineralization. Prior research had shown that ALP transforms a chemical called pyrophosphate, which inhibits mineralization, into another molecule called phosphate, which promotes mineralization.
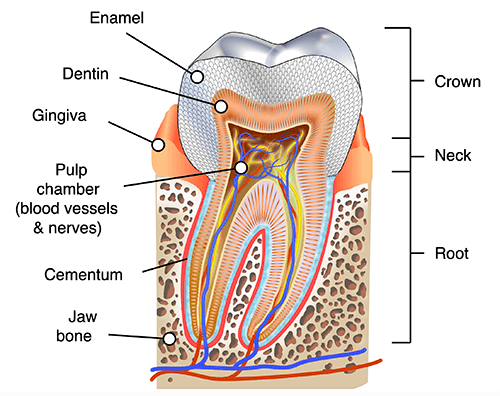
Human tooth diagram-en.svg from Wikimedia Commons by K. D. Schroeder, CC-BY-SA 4.0.
The periodontal ligament (not labeled) connects the cementum to the jaw bone.
The IRP study utilized a mouse model of periodontal disease that lacks the gene for an important bone- and cementum-building protein called bone sialoprotein. The researchers began by giving five-day-old mice a ‘systemic’ therapy that quadrupled their blood’s level of tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase (TNAP), a form of ALP found in bones. At two months of age, the mice that recieved the therapy had cementum that was more than twice as thick as the cementum of their untreated counterparts, and they also showed greater growth of the jaw bone that surrounds the cementum. Moreover, their teeth were just as well-attached to the periodontal ligament as the teeth of untreated, genetically normal mice.
“Bone sialoprotein is thought to be a critical molecule for mineralization,” Dr. Somerman explains, “so this is a perfect proof-of-principle model to examine whether you can regenerate cementum.”
Next, using five-week-old mice with the same genetic defect, Dr. Somerman’s team investigated the effects of delivering TNAP directly to the area where the degraded periodontal tissue was rather than raising TNAP levels in the entire body. The treated animals showed similar beneficial effects to the mice that had received the systemic TNAP-boosting therapy. What’s more, the locally delivered TNAP treatment also promoted growth of the cementum and surrounding jaw bone in genetically normal mice.
A final set of experiments in cells showed that ALP corrected mineralization deficiencies in cementum-producing cells, called cementoblasts, that had the same genetic defect as the mice. However, treating those cells with a chemical that disrupts the transport of phosphate into cells diminished the ALP’s beneficial effects, strongly suggesting that the TNAP treatment given to the mice promoted regeneration of the cementum and surrounding bone by increasing the amount of phosphate available for cementoblasts to use for the rebuilding process.

Dr. Martha Somerman (front-row, left) with members of her lab in 2019.
Moving forward, the IRP scientists will continue refining their TNAP treatment and working to move therapies based on their findings into clinical trials. The fact that TNAP is already FDA-approved for use in humans with genetic TNAP deficiencies could hasten its adoption as a treatment to help rebuild the cementum and jaw bone of people with severe periodontal disease. Importantly, delivering TNAP directly into the damaged area, as the researchers did in their new study, would likely have fewer side effects than introducing it throughout the body.
“We’re incredibly excited about this,” Dr. Somerman says. “Our studies showed that even in a normal mouse that doesn’t have a genetic defect, you can promote the formation of cementum. It is very rewarding to identify factors, such as TNAP, as promising therapies for individuals with periodontal disease.”
Subscribe to our weekly newsletter to stay up-to-date on the latest breakthroughs in the NIH Intramural Research Program.
References:
[1] Delivery of Alkaline Phosphatase Promotes Periodontal Regeneration in Mice. Nagasaki A, Nagasaki K, Kear BD, Tadesse WD, Thumbigere-Math V, Millán JL, Foster BL, Somerman MJ. J Dent Res. 2021 Apr 10; 220345211005677. doi: 10.1177/00220345211005677.
Related Blog Posts
This page was last updated on Tuesday, May 23, 2023
