COVID-19 Timeline at NIH (November–December 2020)
COVID-19 Research and Activities at NIH
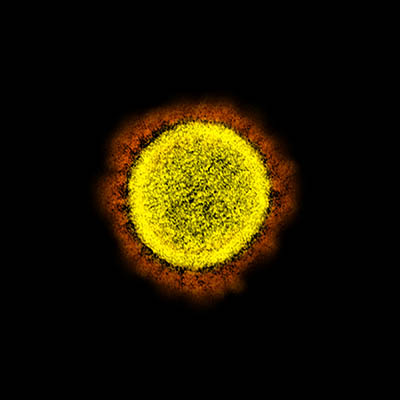
CREDIT: NIAID
Transmission electron micrograph of SARS-CoV-2 virus particles, isolated from a patient. Image captured and color-enhanced at the NIAID Integrated Research Facility (IRF) in Fort Detrick, Maryland.
November 6: NIH Director Francis Collins, in his “all staff” email, acknowledges that election week brings a level of uncertainty and, during an expanding pandemic, it brings a whole new level of anxiety. He also encourages employees to nurture their health and wellbeing, both mental and physical.
November 9: A NIH multicenter, blinded, placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial conducted at 34 U.S. hospitals and involving 479 patients finds that hydroxychloroquine does not benefit adults hospitalized with COVID-19. (JAMA 2020; DOI:10.1001/jama.2020.22240)
November 11: According to a JAMA “Viewpoint” article by NIAID Director Anthony Fauci and colleagues, COVID-19 treatments for people with early infection are needed urgently to speed recovery, reduce the likelihood that they develop severe outcomes, and reduce demand on the health-care system. (JAMA 2020; DOI:10.1001/jama.2020.22813)
November 13: In the NIH Director’s message, Francis Collins announces several research updates for the week: Pfizer announced that early analysis of data on 94 cases in its phase 3 COVID-19 experimental vaccine trial suggests the vaccine is more than 90 percent effective; Moderna signaled that a sufficient number of cases had occurred in the 30,000 participants in their experimental phase 3 trial that the Data and Safety Monitoring Board will be asked to unblind the results in the next few days to assess efficacy; the FDA announces that it has issued an Emergency Use Authorization for the Eli Lilly investigational monoclonal antibody bamlanivimab (LYCoV555) for the treatment of mild-to-moderate COVID-19 in non-hospitalized adult and pediatric patients who are at high risk for progressing to severe disease and hospitalization; NHLBI closes the lid on the use of hydroxychloroquine in hospitalized adults with COVID-19, concluding that the drug provides no clinical benefit in this population. In addition, Collins reports that he and many NIH colleagues met virtually with the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF) to consider the COVID-19 vaccine research and development landscape, rapid detection for SARS-CoV-2, and application of lessons learned to future pandemics; to end the two intense days of Zoom science, BMGF’s Chris Karp and Collins put together a recorded duet of the famous Beatles song “In My Life,” taking liberties with lyrics to add a COVID-19 spin.
November 16: NIH announces that an independent data and safety monitoring board’s interim review of data from Moderna’s investigational COVID-19 vaccine suggests that the vaccine is safe and effective at preventing symptomatic COVID-19 in adults.
November 19: In his message to NIH staff, NIH Director Francis Collins reports on the results of the NIH Workforce COVID-19 Impact Survey Summary.
November 20: NIH has awarded nearly $45 million to expand the research network of the Rapid Acceleration of Diagnostics Underserved Populations (RADx-UP) program, adding 20 institutions and seven states and territories. RADx-UP aims to enable and enhance COVID-19 testing of populations disproportionately affected by the disease, including African Americans, American Indians and Alaskan Natives, Latinos and Latinas, Native Hawaiians, older adults, pregnant women, and those who are homeless or incarcerated.
November 20: NIH holds its sixth Virtual Town Hall to discuss COVID-19-related issues.
November 20: In his “all staff” email, NIH Director Francis Collins cautions people about holiday travel and gatherings and advises people to review the Travel Guidance page on the NIH coronavirus intranet page and to refer to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention guidance on traveling for Thanksgivingand general guidance about holiday celebrations and small gatherings.
November 23: NIH Director Francis Collins performs “Thanksgiving Eve,” adding his own final verse to the folk song written by Bob Franke to thank staff and offer hope during these challenging times: "from the Spring to the Fall, you’ve been heroes one and all, you’ve answered the calls and the cries. Despite the heavy load, your mission has been hope, you’ve done all you could to save lives. I am thankful for our NIH heroes!”
November 25: NIAID announces that the fourth iteration of the Adaptive COVID-19 Treatment Trial has begun to enroll hospitalized adults with COVID-19 who require supplemental oxygen. The NIAID-sponsored trial will enroll up to 1,500 patients at approximately 100 sites in the United States and other countries. [image]
November: NIAID Senior Investigator Elodie Ghedin begins genetic sequencing of SARS-CoV-2 in NIHers who have tested positive for COVID19 and who have given consent. The goal is to determine what variants of the virus are circulating among NIH staff.
December 4: In his email message to staff, Francis Collins announces that HHS, working with NIH and Operation Warp Speed, launched the Combat COVID web portal containing current information on clinical trials that people can participate in, as well as processes for donating blood and plasma, that will lead to prevention and treatment breakthroughs to benefit everyone. In addition, he announces that NIH has rolled out a new app called My COVID-19 Risks that staff can use to help estimate the risk level of activities based on activity type, zip code, health characteristics, and personal risk tolerance.
December 7: An NIBIB-funded tool helps organizations plan COVID-19 testing; an online calculator computes costs of testing and offers strategies for preventing infections in schools and businesses.
December 11: The FDA issues the first Emergency Use Authorization for a vaccine to prevent COVID-19—to Pfizer-BioNTech.
December 11: NIH announces that the combination of baricitinib, an anti-inflammatory drug, and remdesivir, an antiviral, reduced time to recovery for people hospitalized with COVID-19, according to clinical trial results published in the New England Journal of Medicine. The study was supported by NIAID. (New Engl J Med 2020; DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa2031994)
December 15: NIH announces that the FDA granted emergency-use authorization for a rapid at-home COVID-19 test that was developed through the NIBIB RADx initiative and designed by Ellune USA (Valencia, California).
December 16: An observational study has launched to evaluate the short- and long-term health outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 infection in children, including multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C), and to characterize the immunologic pathways associated with different disease presentations and outcomes.
December 16: Vaccine Research Center (VRC) Director John Mascola is named a 2020 Washingtonian of the Year. Mascola and the VRC codeveloped a COVID-19 vaccine with Moderna, building on fundamental research on coronavirus vaccines by Barney Graham, Kizzmekia Corbett, and their colleagues.
December 17: A vaccine advisory group to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration votes that the benefits of the Moderna COVID-19 vaccine outweigh the risks for use in individuals 18 years of age or older, based on the totality of evidence.
December 17: Two randomized, controlled phase 3 clinical trials have begun evaluating investigational monoclonal antibodies for their safety and efficacy in treating people hospitalized with moderate COVID-19.
December 18: HHS Secretary Alex Azar’s email to HHS and NIH staff announces that “[T]hanks to coordination by Operation Warp Speed and CDC, 2.9 million doses of Pfizer’s vaccine were shipped to more than 1,500 sites across America, everywhere from the shores of Guam to the northeastern corner of Maine. This coming week, we have allocated another approximately 2 million doses of Pfizer’s vaccine. On top of that, the FDA has signaled that it plans to authorize the NIH/Moderna vaccine imminently, and we have allocated approximately 5.9 million doses of that product to jurisdictions to ship next week.”
December 18: In NIH Director Francis Collins’s email to NIH staff, he announces that NIAID is starting two randomized, controlled phase 3 clinical trials for monoclonal antibody treatments in hospitalized patients with moderate COVID-19. NIAID also launched an observational study this week to evaluate health outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 infection in children including MIS-C in children. The study is part of a research effort led by NHLBI and NICHD to understand MIS-C.
December 18: The FDA issues an Emergency Use Authorization to Moderna for its COVID-19 vaccine, which was co-developed with scientists at NIAID’s Vaccine Research Center.
December 21: NIH has awarded eight research grants to develop approaches for identifying children at high risk of MIS-C, a rare and severe aftereffect of COVID-19 or exposure to the virus that causes it.
December 21: NIH has awarded over $107 million to support new, nontraditional approaches and reimagined uses of existing tools to address gaps in COVID-19 testing and surveillance. The program also will develop platforms that can be deployed in future outbreaks of COVID-19 and other infectious diseases.
December 22: Preliminary results of a phase 3, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial testing the investigative neutralizing monoclonal antibody LY-CoV555 in hospitalized COVID-19 patients is published today in The New England Journal of Medicine. The antibody did not provide clinical benefit compared with placebo. (New Engl J Med 2020; DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa2033130)
December 22: NIH ACTIV trial of blood thinners pauses enrollment of critically ill COVID-19 patients. Among critically ill COVID-19 patients requiring intensive-care-unit support, therapeutic anticoagulation drugs did not reduce the need for organ support. Enrollment continues for moderately ill hospitalized COVID-19 patients in the trials. NIH and other organizations are funding the trials.
December 22: At the NIH COVID-19 Vaccine Kick-Off Event, six frontline health-care workers at the NIH Clinical Center received the Moderna COVID-19 vaccine codeveloped by researchers at the NIH Vaccine Research Center. In addition, HHS Secretary Alex Azar, NIH Director Francis Collins, NIAID Director Anthony Fauci, and Office of Research Services Director Colleen McGowan also received the vaccine.
December 22: Pregnant women in their third trimester are unlikely to pass SARS-CoV-2 infection to their newborns, according to a study funded by NIH. (JAMA Netw Open 3:e2030455, 2020; DOI:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.30455)
December 22: NINDS neuroscientists isolate promising mini antibodies against COVID-19 from a llama. (Sci Reports 10:Article number 22370, 2020)
December 28: The NIH Division of Occupational Health and Safety opens a vaccine clinic to provide NIH health-care workers with the Moderna COVID-19 vaccine.
December 28: A phase 3 trial of Novavax investigational COVID-19 vaccine opens and will enroll up to 30,000 volunteers. NIAID and HHS’s Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority are funding the trial.
December 30: An NIH study uncovers blood-vessel damage and inflammation in COVID-19 patients’ brains but no infection. (New Engl J Med 2020; DOI:10.1056/NEJMc2033369)
December 30: A peer-reviewed report on Moderna COVID-19 vaccine confirms that the vaccine is 94.1% effective. (New Engl J Med 2020; DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa2035389)
This page was last updated on Thursday, March 10, 2022
