COVID-19 Timeline at NIH (November-December 2022)
COVID-19 Research and Activities at NIH
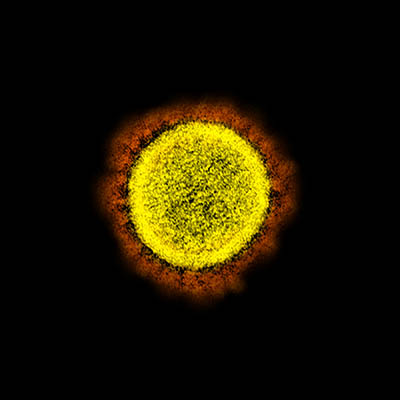
CREDIT: NIAID
Transmission electron micrograph of SARS-CoV-2 virus particles, isolated from a patient. Image captured and color-enhanced at the NIAID Integrated Research Facility in Fort Detrick, Maryland.
November 1: An NIH-funded study finds that blood pressures rose during the pandemic (Hypertension 79:2733–2742, 2022).
November 10: Lawrence Tabak (Performing the Duties of the NIH Director) emails staff with a coronavirus update and warns of a triple threat to public health with influenza, respiratory syncytial virus, and COVID-19 circulating this winter. He reports that NIH will not be pursuing the COVID-19 vaccination requirement for health care workers but urges staff to remain up to date with vaccinations. Tabak reminds staff of NIH guidance on dependent care during duty hours and bringing children onto NIH locations and encourages employees to talk to their supervisors about workplace flexibilities to help balance work and family responsibilities.
November 18: The CDC updates its COVID-19 community levels, moving Phoenix, Arizona, from low to medium. All other NIH locations remain at their current levels.
November 20: NIH scientists speak to National Public Radio about the declining efficacy of monoclonal antibodies against new SARS CoV-2 variants. “Monoclonals had their day, like the Model T or the biplane,” said NIAID’s Carl Dieffenbach, Director of the Division of AIDS and lead of NIH’s Antiviral Program for Pandemics. “Now it’s time to move on.”
November 21: NIAID awards more than $12 million to three institutions for the development of antiviral therapies to treat diseases caused by viruses with pandemic potential.
November 22: NIH launches the MakeMyTestCount.org website, developed through NIH’s Rapid Acceleration of Diagnostics Tech program, which allows users to anonymously report the results of any brand of at-home COVID-19 test.
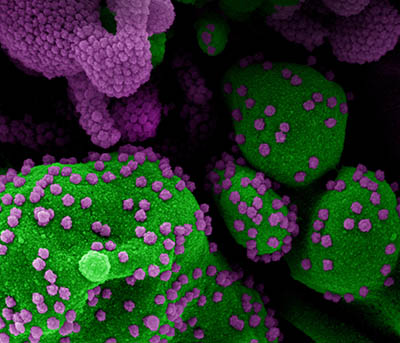
CREDIT: NIAID
Colorized scanning electron micrograph of an apoptotic cell (green) heavily infected with SARS-CoV-2 virus particles (purple), isolated from a patient sample. Image from the NIAID Integrated Research Facility in Fort Detrick, Maryland.
December 1: The New England Journal of Medicine publishes a perspective by NIAID Director Anthony Fauci reflecting on the perpetual challenge of infectious diseases. (N Engl J Med 387:2009-2011, 2022; DOI:10.1056/NEJMp2213814)
December 2: The CDC updates its COVID-19 community levels. Framingham, Massachusetts, moves from low to medium community level and Detroit, Michigan, moves from medium to low. All other NIH locations remain at their current levels.
December 2: The CDC releases a report that associates the drug Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir) with decreased hospitalization rates among adults with COVID-19. A second report releases data showing that the bivalent mRNA vaccines provided significant additional protection against symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection.
December 8: The FDA amends the emergency use authorizations of the bivalent Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccines to include children down to 6 months of age.
December 9: The CDC updates its COVID-19 community levels. Phoenix, Arizona, moves from medium to high community level. Detroit, Michigan, and Rocky Mountain Laboratories in Hamilton, Montana, move from low to medium.
December 9: Lawrence Tabak (Performing the Duties of the NIH Director) emails staff with a coronavirus update, noting that new COVID-19 cases and hospitalizations are increasing nationally. He brings attention to the FDA’s announcement this week authorizing vaccines for children as young as 6 months, as well as CDC data released on December 2 showing the effectiveness of the antiviral Paxlovid and mRNA bivalent boosters.
December 15: The Journal of Clinical Investigation publishes a paper reporting that NIH scientists found that some cancer and autoimmunity drugs may increase susceptibility to infection by respiratory viruses such as SARS-CoV-2 and influenza A (J Clin Invest 132:e160766, 2022; DOI:10.1172/JCI160766).
December 15-16: The FDA and NIH COVID-19 Scientific Interest Group host a virtual COVID-19 research workshop. Scientists from both agencies deliver talks covering recent findings in COVID-19 virology, immunology, therapeutics, and more.
December 16: In an NIH videocast, NIAID Director Anthony Fauci reflects on his 54-year career at NIH, including having advised seven United States presidents, and his commitment to following the science through outbreaks of infectious diseases, from HIV to Ebola to COVID-19. Videocast (NIH only) at: https://videocast.nih.gov/watch=48728.
December 16: The CDC updates its COVID-19 community levels. Baltimore, Maryland (Bayview Research Center), moves from low to medium community level and Phoenix, Arizona, moves from high to medium. All other NIH locations remain at their current levels.
December 19: NIBIB’s RADx Tech program makes available an early version of a best-practices document for developers that provides recommendations for making at-home COVID-19 diagnostic kits accessible to all users including people with no vision or low vision, a reduced range of dexterity or motor skills, and those who are aging.
December 23: The CDC updates its COVID-19 community levels. Montgomery County, Maryland, moves from low to medium community level and Rocky Mountain Laboratories in Hamilton, Montana, moves from medium to low.
December 30: All NIH locations are at medium in CDC’s COVID-19 community level classification.
This page was last updated on Sunday, January 8, 2023
