COVID-19 Timeline at NIH (July–August 2022)
COVID-19 Research and Activities at NIH
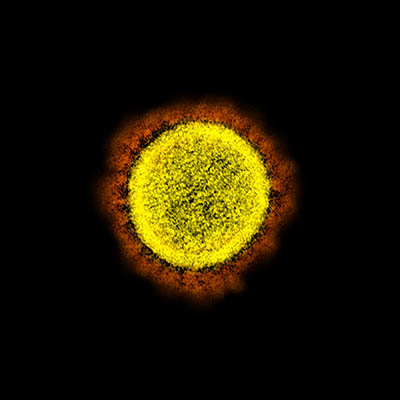
CREDIT: NIAID
Transmission electron micrograph of SARS-CoV-2 virus particles, isolated from a patient. Image captured and color-enhanced at the NIAID Integrated Research Facility (IRF) in Fort Detrick, Maryland.
July 1: The CDC updates its COVID-19 community levels. Bayview Research Center, Baltimore, Maryland, transitions from low to medium community level and Phoenix, Arizona, moves from medium to high. All other NIH locations remain at their current levels.
July 5: An analysis led by NCI researchers finds that COVID-19 was the third leading cause of death in the United States between March 2020 and October 2021 (JAMA Intern Med 182:883–886, 2022).
July 5: An NINDS team of researchers led by Avindra Nath publishes a study describing an immune response triggered by COVID-19 infection that damages the brain’s blood vessels and may lead to short- and long-term neurological symptoms (Brain awac151, 2022; DOI:10.1093/brain/awac151).
July 6: The FDA revises the Emergency Use Authorization for the antiviral pill Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir with ritonavir) to authorize state-licensed pharmacists to prescribe the drug to eligible patients, with certain limitations.
July 8: Acting NIH Director Lawrence Tabak emails staff to announce that NIH expects to start implementing the NIH COVID-19 Vaccination Policy for the Healthcare Workforce, as required by HHS policy. He mentions the previous week’s FDA recommendation that advised manufacturers to develop a two-component booster vaccine to provide protection against circulating and emerging variants in the fall and winter months. Tabak also highlights NIH COVID-19 research updates released earlier this week.
July 9: The CDC moves Phoenix, Arizona, from high to medium COVID-19 community level. All other NIH locations remain at their current levels.
July 14: In a recent study, NCI researchers and their collaborators find that interferon treatment may reduce severity of COVID-19 in people with certain genetic factors (Nat Genet 54:1103–1116, 2022).
July 15: The CDC moves Phoenix, Arizona, from medium back to high COVID-19 community level. All other NIH locations remain at their current levels.
July 19: A clinical trial sponsored by NIAID finds that neutralizing antibody concentrations against the omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 decrease substantially in adults within three months of receiving a booster vaccination (Cell Rep Med 3:100679, 2022).
July 19: The CDC recommends that Novavax’s protein-based COVID-19 vaccine be used as another primary series option for adults in the United States ages 18 years and older. The vaccine was developed with support from NIAID. “This is the third COVID-19 vaccine available in the [United States] as a result of the unprecedented government research response to develop safe and effective COVID-19 vaccines, for which NIH spearheaded the clinical testing,” says Lawrence Tabak, whose new title, effective July 17, is “Performing the Duties of the Director of NIH.” Federal requirements limit the time anyone can serve as “acting” in a presidentially appointed position. Tabak’s duties remain unchanged, and he will once again be “acting NIH director” when President Biden nominates a new NIH Director and until that new director is confirmed by the U.S. Senate.
July 19: A trans-NIH collaborative study supported by NIAMS, NIAID, NIDCR, and NCI finds that disruptions in neutrophil biology are associated with the pathogenesis and severity of COVID-19 in children and adults (JCI Insight 2022; DOI:10.1172/jci.insight.160332).
July 21: President Biden tests positive for COVID-19. He is fully vaccinated and twice boosted and experiencing very mild symptoms. He has begun taking Paxlovid. Consistent with CDC guidelines, he will isolate at the White House and will continue to carry out all his duties fully during that time.
July 22: Lawrence Tabak (Performing the Duties of the Director of NIH) emails staff with a coronavirus update. He continues to expect that NIH will implement the COVID-19 Vaccination Policy for Healthcare Workforce, as required by HHS policy, in the coming weeks. Tabak also highlights this week’s CDC recommendation of Novavax’s protein-based COVID-19 vaccine, which was developed with the support of NIAID scientists and their collaborators.
July 29: The CDC updates Detroit, Michigan, from low to high COVID-19 community level. All other NIH locations remain at their current levels.
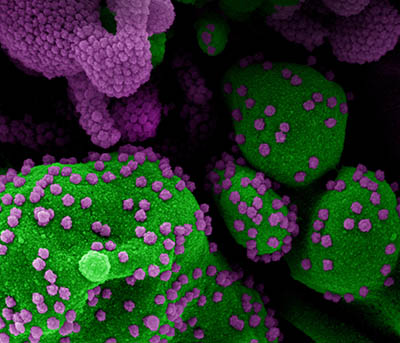
CREDIT: NIAID
Colorized scanning electron micrograph of an apoptotic cell (green) heavily infected with SARS-CoV-2 virus particles (purple), isolated from a patient sample. Image from the NIAID Integrated Research Facility (IRF) in Fort Detrick, Maryland.
August 5: The CDC updates its COVID-19 community levels. Montgomery County, Maryland, moves from medium to high, Rocky Mountain Labs in Hamilton, Montana, moves from medium to low, and Phoenix, Arizona, moves from high to low community level. All other NIH locations remain at their current levels.
August 5: In an email to all staff, Lawrence Tabak (Performing the Duties of the Director of NIH) remarks on the increase of COVID-19 community levels across the United States driven by the omicron subvariant BA.5. With Montgomery County, Maryland, moving to high community level, he reviews safety requirements when reporting onsite for all staff as laid out in the NIH Safety Plan. All staff are required to wear a mask; maintain 6 feet of physical distance; follow the guidance on density limits specified on the Physical Distancing and Onsite Density Requirements webpage; test weekly if partially vaccinated, unvaccinated, or have not reported vaccination status; submit the NIH COVID-19 In-Person Meeting/Event Safety Plan for all in-person meetings and events regardless of size. The CDC COVID-19 community level reporting now gives NIH the information needed to inform workplace mitigation efforts, and the NIH staff COVID-19 surveillance charts will be removed from the Guidance for NIH Staff on Coronavirus intranet site.
August 12: The CDC updates its COVID-19 community levels. NICHD in Detroit, Michigan, moves from high to medium community level and Rocky Mountain Laboratories in Hamilton, Montana, moves from low to medium. All other locations remain at their current levels.
August 17: NIH updates its COVID-19 safety plan for meetings and testing requirements based on CDC’s updated recommendations. Employees and visitors entering NIH facilities or attending NIH-sponsored meetings will not be asked to disclose any information regarding vaccination status or be asked to present a negative COVID-19 test. Additionally, there is no longer a testing requirement for unvaccinated staff when the COVID-19 community level is at medium or high. Staff who have had a COVID-19 exposure and are not experiencing symptoms are permitted to come onsite but are required to wear a mask for 10 days after exposure and get tested on day 5. These updates do not apply to health care workers, who remain subject to more stringent requirements.
August 19: The CDC updates its COVID-19 community levels. Montgomery County, Maryland, moves from high risk to low and NICHD in Detroit, Michigan, moves from medium back to high. All other NIH locations remain at their current levels.
August 19: Lawrence Tabak (Performing the Duties of the Director of NIH) emails staff with a coronavirus update. He reviews NIH’s updated COVID-19 safety plan announced on August 17. The new plan reflects the CDC’s streamlined recommendations for non-health-care workers regarding quarantine requirements after exposure and no longer requires testing or reporting of vaccination status when entering NIH facilities or to participate in NIH-sponsored meetings.
August 22: Anthony Fauci announces that, in December 2022, he will stepping down from the positions of NIAID director and chief of the NIAID Laboratory of Immunoregulation, as well as the position of Chief Medical Advisor to President Joe Biden. He states that he is not retiring but plans to pursue the next phase of his career and use what he had learned as NIAID director to continue to advance science and public health and to inspire and mentor the next generation of scientific leaders as they help prepare the world to face future infectious disease threats. Fauci, who is 81 years old, has spent 54 years at NIH, 38 as the NIAID director, advising seven U.S. Presidents, and reassuring the public as America’s doctor during outbreaks of infectious diseases, from HIV to Ebola to COVID-19.
August 26: A study funded by NIH’s Rapid Acceleration of Diagnostics Tech program finds that with age-appropriate instructions, school-aged children can successfully use a nasal swab to obtain their own COVID-19 test specimen. The study provides data to support recommendations regarding self-swabbing that can be implemented by schools and in other settings where children undergo COVID-19 testing (JAMA 2022; doi:10.1001/jama.2022.14877).
August 29: A NIAID-led team of researchers finds that the amount of SARS-CoV-2 antigen measured in the blood of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 is associated with illness severity and other clinical outcomes (Ann Intern Med 2022; DOI: 10.7326/M22-0924).
August 30: A team from NCATS, NIEHS, and the Naval Research Laboratory reports that they have built a library of small antibodies, called synthetic nanobodies, and used it to find promising new therapeutic leads for halting viral activity. They have identified three nanobodies that appear to be most effective in blocking SARS-CoV-2 infection (PLoS One 2022; DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0272364).
August 31: The FDA authorizes bivalent formulations of the Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccines for use as a single booster dose at least two months after completing primary or booster vaccination. The updated COVID-19 vaccine boosters are designed to give broad protection against COVID-19, including better protection against the Omicron variant
This page was last updated on Monday, September 19, 2022
