COVID-19 Timeline at NIH (May-June 2021)
COVID-19 Research and Activities at NIH
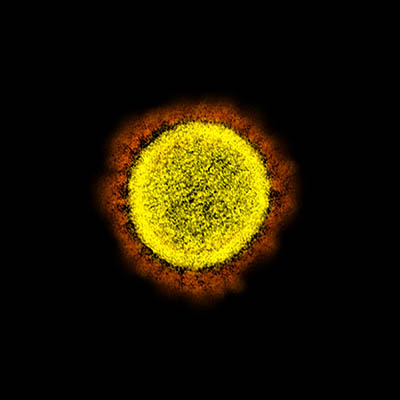
CREDIT: NIAID
Transmission electron micrograph of SARS-CoV-2 virus particles, isolated from a patient. Image captured and color-enhanced at the NIAID Integrated Research Facility (IRF) in Fort Detrick, Maryland.
May 3: A study led by NHLBI, NIDDK, NIAID, and NCI finds a proinflammatory immune pathway that affects the lungs of patients with severe COVID-19. Researchers used lab and computer models to test treatments that could help patients with severe lung infections recover faster. The study is published in Science Immunology. (Sci Immunol 6:issue 58, eabg0833, 2021; DOI:10.1126/sciimmunol.abg0833)
May 7: In an all-staff email, NIH Director Francis Collins reports that a pilot study has been launched at NIAID’s Rocky Mountain Labs (Hamilton, Montana) that will detail the process for slowly increasing the density of scientific and technical staff in the labs.
May 10: The FDA expands its emergency-use authorization for the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine to include adolescents 12–15 years of age. In his all-staff email later this week, NIH Director Francis Collins says: “With more than 17 million adolescents in the U.S., vaccination of this age group will not only help protect them from COVID-19 but also help stop the spread of the virus.”
May 10: The NIH Clinical Center updates its visitor policy, which had restricted visitors during the COVID pandemic: Adult inpatients may have one visitor at a time. Pediatric inpatients are allowed two visitors at a time, as are inpatients near the end of life. New adult outpatients can bring one escort or attendant, and pediatric outpatients (new or returning) can have two adults accompany them.
May 11: NIAID Director Anthony Fauci and CDC Director Rochelle Walensky testify before the Senate Health, Education, Labor, and Pensions Committee on efforts to combat COVID-19.
May 12: Outdoor dining returns to campus. Eurest Dining Services will prepare a rotating, themed barbecue for lunch every other Wednesday on the south lawn of Building 10.
May 13: The CDC updates its mask guidance: Except where locally required, fully vaccinated people can resume activities outdoors and indoors without wearing a mask or physically distancing. The new guidance is based on data showing that COVID-19 cases have decreased, that vaccines are effective against the current variants, and that fully vaccinated individuals are far less likely to spread the virus. In an NIH-wide email later this week, Director Francis Collins asks for staff to be patient and continue to wear a mask at work as the new guidance does not yet apply to health-ocare settings such as NIH premises.
May 13: The Trans-NIH Mental Health Response Team launches a new “How I Cope with Stress” campaign. Employees are encouraged to support one another by sharing how they cope with stress on social media using the hashtag #NIHCopeWithStress.
May 14: In his email to all employees, NIH Director Francis Collins recognizes the ongoing efforts of The Trans-NIH Mental Health Response Team for Mental Health Awareness Month and shares additional mental-health resources.
May 17: Eight U.S. Senators (many are members of the Appropriations Committee) and their staff tour the Vaccine Research Center to learn about the rapid development of safe and effective COVID-19 mRNA vaccines, now in distribution throughout the world. Senators are also briefed on the RADx pipeline of new COVID-19 testing technologies, and about emerging research on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on mental health. The tour concludes with a high-level conversation about a new potential unit of NIH called ARPA-H, a top priority of the Biden Administration to push the boundaries of science.
May 19: In an all-staff email, NIH director Francis Collins updates mask guidance to allow unmasking in outdoor spaces where physical distancing is possible. Outdoor gatherings will continue to be limited to 50 people. He reports that the staff vaccination rate stands at 65% and masks will continue to be required inside all NIH buildings, except in rooms occupied by one person.
May 21: In his all-staff email, NIH Director Francis Collins announces NIH is joining HHS sibling agencies and the White House in a digital day of action to distribute vaccine information and resources across all digital platforms, as part of the “We Can Do This” campaign. He continues to encourage employees to take advantage of the asymptomatic testing center on the fifth floor of the Clinical Center.
May 25: NIH Director Francis Collins testifies virtually before the U.S. House of Representatives Labor, Health and Human Services Subcommittee hearing on the Fiscal Year 2022 NIH Budget, providing an opportunity to discuss a range of topics, including COVID-19, health disparities, and substance abuse.
May 26: Alongside several NIH leaders, NIH Director Francis Collins testifies in-person before the U.S. Senate Appropriations Subcommittee on Labor, Health and Human Services, Education, and Related Agencies at a hearing titled “National Institutes of Health’s FY22 Budget and the State of Medical Research.” A wide range of topics are discussed surrounding the funding needed to advance biomedical research at NIH, including efforts to end the current COVID-19 pandemic. Among those present are NIH institute directors Anthony Fauci(NIAID), Diana Bianchi (NICHD), Ned Sharpless (NCI), Gary Gibbons (NHLBI), Eliseo Pérez-Stable (NIMHD), Bruce Tromberg (NIBIB), and Nora Volkow (NIDA).
May 28: NIH Director Francis Collins sends his 85th pandemic-related email to staff. He announces the application process for Group C federal employees, fellows, and trainees to return to the physical workspace will be reinitiated (it was first announced in October 2020 and then paused). Those who are interested in voluntarily returning will be offered the opportunity to apply for consideration by their supervisor and executive officer.
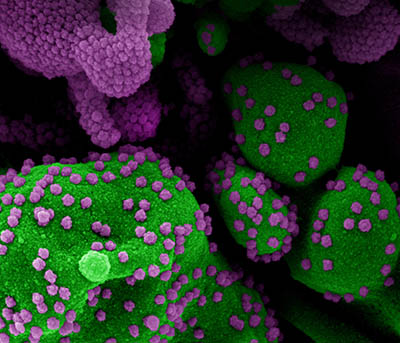
CREDIT: NIAID
Colorized scanning electron micrograph of an apoptotic cell (green) heavily infected with SARS-COV-2 virus particles (purple), isolated from a patient sample. Image at the NIAID Integrated Research Facility (IRF) in Fort Detrick, Maryland.
June 1: A study led by NHLBI and NIAID finds that SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, does not appear to pose a threat to the safety of the nation’s blood supply. (Transfusion 2021; DOI:10.1111/trf.16511)
June 1: NIAID initiates a clinical trial in which adult volunteers who have been fully vaccinated against COVID-19 will receive booster doses of different COVID-19 vaccines to determine the safety and effectiveness of mixed booster regimens. “The results of this trial are intended to inform public health policy decisions on the potential use of mixed vaccine schedules should booster doses be indicated,” said NIAID Director Anthony Fauci in a news release.
June 1: NIH Director Francis Collins announces in his blog that two NIH-supported studies found that that COVID-19 mRNA vaccines are safe and effective for pregnant women with the potential to benefit both mother and baby. (JAMA 325:2370–2380, 2021; DOI:10.1001/jama.2021.7563 and Obstet Gynecol 2021; DOI:10.1097/AOG.0000000000004457)
June 2: The Employee Asymptomatic Testing Clinic on the 5th floor of the Clinical Center will no longer be open on Wednesdays; there will be no changes to evening and weekend hours.
June 3: An NICHD-led study published in Science finds that the experimental drug TEMPOL may be a promising oral antiviral treatment for COVID-19. TEMPOL can limit SARS-CoV-2 infection by impairing the activity of a viral enzyme called RNA replicase. (Science, eabi5224, 2021; DOI:10.1126/science.abi5224)
June 3: An NIH Director’s Blog post reports that NIH-funded researchers have discovered a way to detect where COVID-19 hotspots are emerging by measuring viral load in a positive COVID-19 diagnostic test. (Science, eabh0635, 2021; DOI:10.1126/science.abh0635)
June 8: In his Director’s Blog, Francis Collins announces that new NIH-supported studies, published in Cell Metabolism, found that some people can develop diabetes after an acute COVID-19 infection; SARS-CoV-2 can target and impair the body’s insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas and may even change the function of surviving cells. (Cell Metab S1550-4131(21)00232-1, 2021; doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2021.05.015); (Cell Metab S1550-4131(21)00230-8, 2021; doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2021.05.013)
June 11: In the NIH Director’s all-staff email, Francis Collins announces that more than 80.4% of all NIH staff have received at least one dose of the vaccine. He also explains that the NIH COVID-19 vaccine clinic will be reducing its hours (see below). He gives special thanks to staff who screened people entering the Clinical Center and ran the asymptomatic testing clinic. From March 2020 through June 3, 2021, more than 1.4 million people were screened to enter the Clinical Center; from May 2020 through June 3, 2021, the asymptomatic testing clinic ran more than 111,713 tests.
June 14: Until now NIH’s Occupational Medical Health Service (OMS) has been operating a daily COVID-19 vaccine clinic in the Clinical Center’s B-1 cafeteria. In light of decreased demand, the COVID-19 vaccines will now be offered once a week, on Thursdays, in the OMS Clinic in Room 6C306 through August for new employees, fellows, and other staff.
June 14: A phase 3 clinical trial in the United States and Mexico shows that the investigational vaccine NVX-CoV2373 developed by Novavax, Inc. (Gaithersburg, Maryland), demonstrated 90.4% efficacy in preventing symptomatic COVID-19 disease and showed 100% protection against moderate and severe disease. The trial enrolled adult volunteers at 119 study sites including those in the NIAID-supported COVID-19 Prevention Network.
June 15: The NIH Clinical Center’s Acting Chief Medical Officer Colleen Hadigan updates pre-procedure testing guidelines for asymptomatic patients without known high-risk COVID-19 exposure: NIH patients undergoing dental procedures, imaging procedures under local anesthesia, nasal or oral endoscopy, pulmonary function testing, strenuous exercise testing, and swallow studies will no longer require SARS-CoV-2 pre-procedure testing.
June 15: NIH Director Francis Collins highlights a new NIH-supported study that found a specifically engineered antibody delivered by a nasal spray dramatically reduced the amount of SARS-CoV-2 in the lungs of mice. (Nature 2021; DOI:10.1038/s41586-021-03673-2)
June 15: An NIH-led study finds evidence of SARS-CoV-2 infections in five U.S. states as early as December 2019, weeks prior to the first recognized cases. Researchers identified SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in blood specimens sampled from participants in the ongoing “All of Us” study that were taken in all 50 U.S. states from January 2 to March 18, 2020. (Clin Infects Dis ciab519, 2021; DOI:10.1093/cid/ciab519)
June 15: The day-long “NIH Summit on Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies for Treatment and Prevention of COVID-19: Lessons Learned and Remaining Questions” begins with opening remarks from NIH Director Francis Collins, Acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock, and NIAID Director Anthony Fauci. The event features presentations on the current state of the science and sessions addressing the design, development, and real-world use of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies.
June 17: The Biden Administration announces it will invest more than $3 billion to accelerate the discovery, development, and manufacturing of antiviral medicines as part of a strategy to develop the next generation of COVID-19 treatments. Called the Antiviral Program for Pandemics, the HHS- and NIAID-led initiative will respond to the urgent need for antivirals to treat COVID-19 and will also will build sustainable platforms for discovery and development of antivirals for other viruses with pandemic potential, helping better prepare the nation to face future viral threats.
June 21: In an all-staff email, NIH Principal Deputy Director Lawrence Tabak announces that Group C federal employees, fellows, and trainees may now apply to voluntarily return to the physical workspace; applications will have to be approved before individuals can return.
June 22: In his blog, NIH Director Francis Collins explains how a new NIH-supported study attempted to answer the question of how immunity generated from COVID-19 vaccines differs from an infection. The data indicate that people who’ve had and recovered from COVID-19 still stand to benefit from getting vaccinated. (Sci Transl Med eabi9915, 2021; DOI:10.1126/scitranslmed.abi9915)
June 22: An NIH team of researchers report that the prevalence of COVID-19 in the United States during the spring and summer of 2020 far exceeded the known number of cases and that there were nearly 17 million undiagnosed cases by mid-July. (Sci Transl Med eabh3826, 2021; DOI:10.1126/scitranslmed.abh3826)
June 23: NIAID begins a new observational study called MOMI-VAX designed to measure the development and durability of antibodies against SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, in people vaccinated during pregnancy or the first two postpartum months. Researchers also will assess vaccine safety and evaluate the transfer of vaccine-induced antibodies to infants across the placenta and through breast milk.
June 24: A NIDA-funded study finds that adolescent marijuana use and binge drinking did not significantly change during the COVID-19 pandemic despite record decreases in the perceived availability of marijuana and alcohol. The findings, based on a survey of 12th graders in the United States, challenge the idea that reducing adolescent use of drugs can be achieved solely by limiting their supply. (Drug Alcohol Depend 2021; DOI:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2021.108822.)
June 24: In his blog, NIH Director Francis Collins announces that NIH-funded researchers have developed a new metric to more accurately detect where COVID-19 hotspots are emerging. (Science eabh0635, 2021; DOI:10.1126/science.abh0635)
June 29: NIH announces that an adjuvant developed with NIH funding has contributed to the success of the highly efficacious COVAXIN COVID-19 vaccine, which was developed and is manufactured in India.
June 30: NIH reports that researchers (including NIBIB) affiliated NIH’s Rapid Acceleration of Diagnostics (RADx) initiative found that both the rapid antigen tests and PCR molecular testing methods were equally effective in detecting SARS-CoV-2 infection when tests were given every three days. (J Infect Dis 2021; DOI:10.1093/jid/jiab337)
June 30: The NIH Director’s Blog continues to cover COVID-19 and the work being done by NIH and NIH-funded researchers.
This page was last updated on Thursday, February 3, 2022
