Middle-Age Weight and Fitness Changes
Blame Your Enzyme
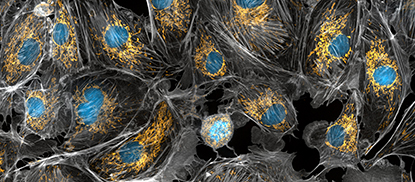
CREDIT: TORSTEN WITTMANN, UNIVERSITY OF SAN FRANCISCO
As people age, the DNA-PK enzyme becomes overactive, causing a decrease in the number of mitochondria and promoting weight gain. Shown: Mitochondria stained bright yellow, cell nuclei in blue, and the cell cytoskeleton in gray.
Researchers have long known that losing weight and maintaining the capacity to exercise tend to get harder beginning between ages 30 and 40—the start of midlife. Scientists have developed new therapies for obesity, including fat-fighting pills. However, many therapies have failed because of a lack of understanding of the biological changes that cause middle-aged people to gain weight, particularly around the abdomen.
Jay H. Chung, an endocrinologist at the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), was always puzzled by the aging weight-gain paradox. An average adult in America gains 30 pounds from age 20 to 50, even though food intake usually decreases during this period. Chung and his team of researchers—from NHLBI, the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, and five universities—thus searched for biochemical changes in middle-aged animals (human equivalent of 45 years old). Their study appeared on May 2, 2017, in Cell Metabolism.
The team focused on an enzyme called DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK), which is activated by a specific kind of DNA damage. Evidence has been mounting, however, that DNA-PK has functions beyond DNA repair and can even affect metabolism.
The scientists looked at levels of DNA-PK activity in the skeletal muscles of rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta), mice, and rats. Activity was low over time until middle age, when it rose significantly. Further experiments showed that DNA-PK activity promotes the conversion of nutrients to fat and decreases the number of mitochondria, the tiny organelles in cells that turn fat into energy to fuel the body.
Mitochondria can be found in abundance among young people, but the numbers drop considerably in older people. Researchers know that fewer mitochondria can promote obesity as well as loss of exercise capacity.
The researchers theorized that reducing DNA-PK activity might increase the number of mitochondria and promote fat burning. They tested their theory in mice with a drug that inhibits DNA-PK. Mice that received the inhibitor gained 40 percent less weight when fed a high-fat diet. The drug boosted the number of mitochondria in the skeletal muscle, increased the fitness of obese and middle-aged mice, and reduced the incidence of obesity and type 2 diabetes.
The team also examined the role of DNA-PK activity in calorie restriction and aerobic fitness, both of which can delay aging and protect against chronic diseases in animal models. Rhesus macaques on a calorie-restricted diet had lower DNA-PK activity in skeletal muscle. Rats selectively bred to be strong runners also had three-fold lower DNA-PK concentrations in their skeletal muscle than did the poor runners.
“Our society attributes the weight gain and lack of exercise at midlife—approximately 30–60 years—primarily to poor lifestyle choices and lack of willpower,” said Chung. “But this study shows that there is a genetic program driven by an overactive enzyme that promotes weight gain and loss of exercise capacity at midlife.”
These findings could lead to the development of a new type of weight-loss medication. However, DNA-PK inhibitors have yet to be tested for this purpose in humans. Middle-aged people who are fighting obesity should continue to reduce calories and boost exercise, according to the researchers.
This article is adapted from one that appeared in NIH Research Matters on May 12, 2017 (http://bit.ly/2uz7j6k).
Reference: NIH authors: S.J. Park, O. Gavrilova, A.L. Brown, J. Kim, X. Xu, S. Yang, J.H. Um, M.K. Kim, and J.H. Chung, Cell Metab 25:1135–1146.e7. DOI:10.1016/j.cmet.2017.04.008, (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28467930)
This page was last updated on Monday, April 11, 2022
