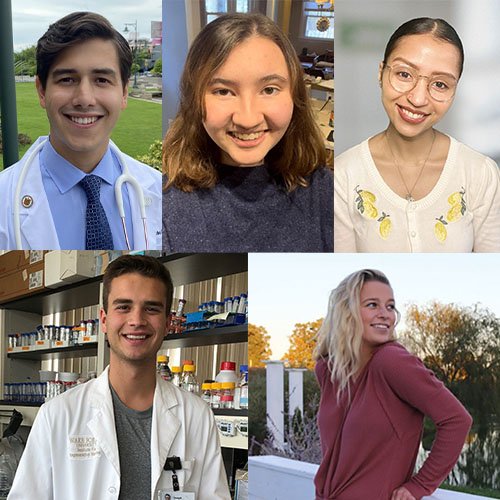
A Peek at This Year’s Postbac Poster Day
Annual Event Provides Showcase for IRP Postbaccalaureate Fellows
As informative as undergraduate science courses can be, there’s no better way to learn the ins and outs of biology than to scrutinize and manipulate it in the lab every day. That’s why so many science enthusiasts flock to NIH after college to participate in the IRP Postbaccalaureate IRTA Program, which allows newly minted grads to spend a year or two working full-time in a lab at NIH. And rather than demonstrating the knowledge they’ve gained on a test, IRP postbacs get to present their research at NIH’s Postbac Poster Day each year, an environment akin to the poster sessions at scientific conferences many postbacs will be attending as they continue their scientific careers.
This year, more than 900 IRP postbacs showed off their research at the event, and unlike prior years, all their presentations were done during one absolutely jam-packed day rather than being spread over two days. Read on to learn about how five of them have taken advantage of the opportunity to work in IRP labs over the past year.