Reining in Runaway Enzyme Halts Neuronal Destruction
Mouse Study Supports Potential Treatment Approach for Numerous Neurological Diseases
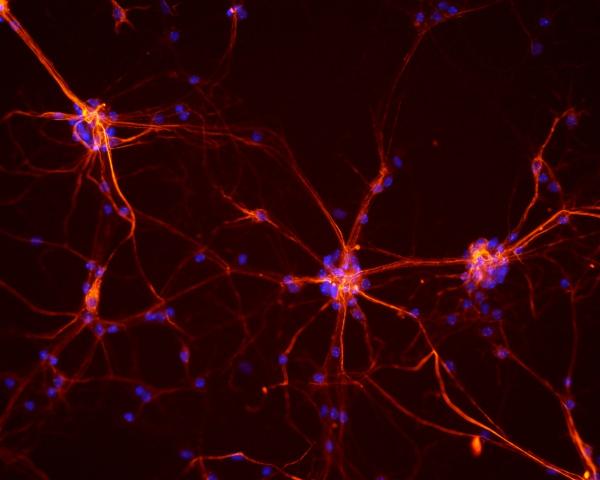
Winter is fast approaching, bringing with it both picturesque snow flurries and raging blizzards. It's a good reminder that something that is desirable in moderate amounts can be downright dangerous in large quantities, and the systems that keep our cells healthy are no different. IRP researchers recently found a novel way to tamp down a runaway cellular process that can kill neurons, findings that may one day lead to new treatments for several debilitating neurological conditions.