Leveraging Turncoat Immune Cells to Combat Cancer
IRP Researchers Develop Drug to Recapture Immune Cells Hijacked by Tumors
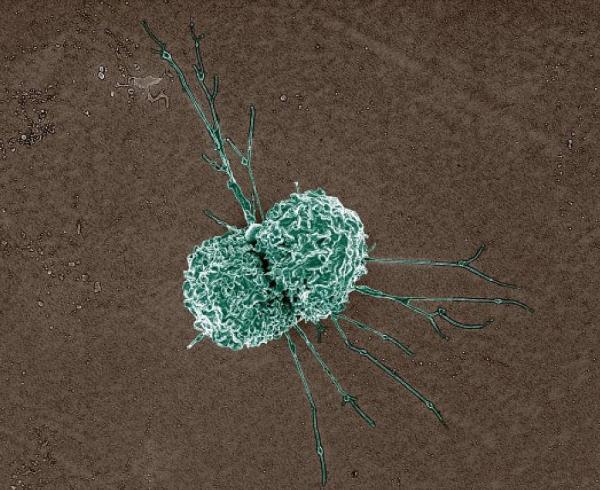
In the 1958 cult classic The Blob, a giant gelatinous creature from outer space lands on Earth and begins engulfing a small town and everything in it. While that may sound far out, a similar entity within our bodies does much the same thing, but for good instead of ill. These Pac-Man-like blobs are called macrophages — Greek for ‘big eaters’ — and they serve a vital role in keeping us healthy by clearing away dead cells and digesting foreign invaders like bacteria and cancer cells.
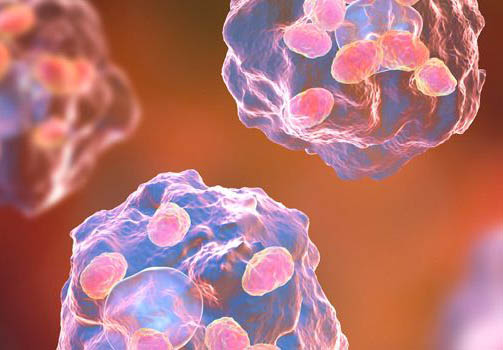
However, cancer cells aren’t content to just let themselves be eaten. They have evolved ways to overwhelm and commandeer the immune system, redirecting immune cells to support tumor growth rather than suppress it. Although highly personalized ‘immunotherapies’ that reboot the immune response and harness it to fight cancer have made significant advances in treating some forms of the disease, most cancers do not respond to these treatments. Fortunately, reinforcements are on the way: IRP senior investigators Udo Rudloff, M.D., Ph.D., and Juan Marugan, Ph.D., have identified a way to reclaim the loyalty of macrophages that are aiding and abetting tumors, turning them back into the cancer-consuming gluttons they were meant to be. Importantly, this approach may be effective on a broader array of cancers than other immunotherapies.