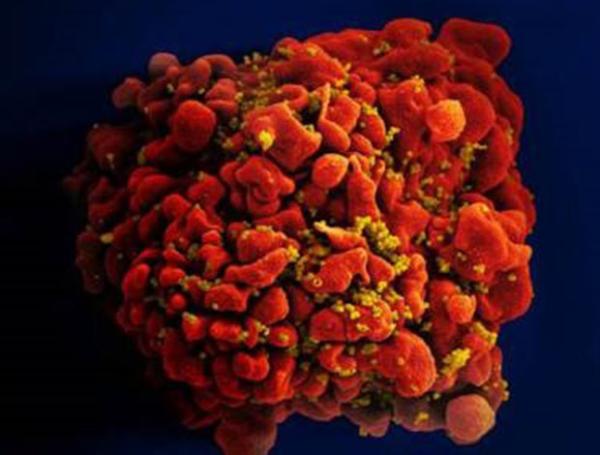
HIV Uses Host's Own Immune Molecules for Protection
In one of Aesop’s classic fables, a clever wolf dons a sheep’s skin in order to move through the herd undetected. As it turns out, IRP researchers have discovered that in people with a specific set of immune system genes, the HIV virus uses a similar approach to hide from the body’s defenses.1
Nearly all cells in our bodies are coated with proteins called human leukocyte antigens (HLAs). These proteins allow the immune system to distinguish between healthy, native cells and those contaminated by unwelcome visitors like viruses or bacteria that must be destroyed. Each of the various HLA proteins is encoded by a different HLA gene and these genes vary considerably between individuals, causing different people to have different variants of each HLA protein.
“There are thousands of different forms of these HLA genes, and that variation allows us, as a species, to deal with virtually all infectious pathogens,” says IRP Senior Investigator Mary N. Carrington, Ph.D., the senior author of the new paper. “We’re really interested in the diversity of that part of the genome, since the risk of essentially every autoimmune disease, many cancers, and probably every infectious disease is associated with this set of genes.”