COVID-19 Timeline at NIH (September–October 2020)
COVID-19 Research and Activities at NIH
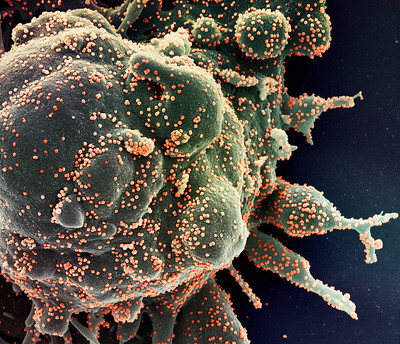
CREDIT: NIAID
Colorized scanning electron micrograph of an apoptotic cell (green) heavily infected with SARS-COV-2 virus particles (orange), isolated from a patient sample. Image captured at the NIAID Integrated Research Facility (IRF) in Fort Detrick, Maryland.
September 1: NIH launches a study to track the prevalence and impact of SARS-CoV-2 infection among approximately 16,000 pregnant women in seven low- and middle-income countries.
September 2: NIH announces $129.3 million in scale-up and manufacturing support for a new set of COVID-19 testing technologies as part of its Rapid Acceleration of Diagnostics (RADx) initiative. NIH is awarding contracts to nine companies for technologies that include portable point-of-care tests for immediate results and high-throughput laboratories that can return results within 24 hours. These tests add to initial awards made to seven companies on July 31, 2020.
September 9: NIH Director Francis Collins and U.S. Surgeon General Jerome M. Adams testify at a Senate Health, Education, Labor, and Pensions Committee on “Vaccines: Saving Lives, Ensuring Confidence, and Protecting Public Health.”
September 10: NIH ACTIV (Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines) initiative launches two of three adaptive clinical trials of blood-clotting treatments for COVID-19. These trials will be conducted at more than 100 sites around the world and will involve patients who have not been hospitalized, those currently hospitalized, and those discharged after hospitalization for moderate to severe disease.
September 11: NIH Director Francis Collins’s email to staff mentions that AstraZeneca phase 3 investigational COVID-19 vaccine trial was put on a clinical hold because of an adverse event in one volunteer at a site in the United Kingdom. In the meantime, the Moderna and Pfizer phase 3 investigational vaccine trials continue to move forward. Collins also announces the launch of a brief survey to do a “pulse check” on how many employees have telework situations that are not ideal and would like to work on-site on a voluntary basis if local circumstances allowed NIH to return additional staff.
September 14: NIDA Director Nora D. Volkow coauthored a study that found that people with substance-use disorders are more susceptible to COVID-19 and its complications. (Mol Psychiatry 2020; DOI:10.1038/s41380-020-00880-7).
September 14: NIH Clinical Center begins offering saliva testing as an option for asymptomatic employees. The mid-turbinate test will still be offered.
September 15: NIH awards contracts to develop innovative digital health technologies for COVID-19.
September 16: NIH funds community engagement research efforts in areas hardest hit by COVID-19.
September 22: NIH expands clinical trials to test convalescent plasma against COVID-19.
September 23: Fourth large-scale COVID-19 vaccine trial begins in the United States. The trial will evaluate a single-dose vaccine.
September 23: NIAID Director Anthony Fauci testifies at a U.S. Senate Health, Education, Labor, and Pensions Committee hearing on “COVID-19: An Update on the Federal Response.”
September 23: The Office of Research Services announces that NIH staff working on campus can use the Eatify app to remotely order and pay for food from the Building 35 cafeteria or the Clinical Research Center Coffee Bar (Building 10 staff only). Food truck services are also continuing in Lot 10H behind Building 10 and outside Building 35 as long as weather allows.
September 24: NIH scientists and others announce their discovery of the genetic and immunologic underpinnings of some cases of severe COVID-19. (Science 370:eabd4570, 2020; DOI:10.1126/science.abd4570; Science 370:eabd4585, 2020; DOI:10.1126/science.abd4585).
September 29: NIH reports that the phase 1 trial of Moderna’s investigational vaccine, which was codeveloped with NIAID, shows that the vaccine is well-tolerated and generates an immune response in adults over 70 years old. (N Engl J Med 2020; DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa2028436).
September 30: As part of the Rapid Acceleration of Diagnostics (RADx) initiative, NIH awards nearly $234 million to improve COVID-19 testing for underserved and vulnerable populations. The program will support 32 institutions in the United States.
October 1: NIAID Director Anthony Fauci is awarded the Service to America Medal 2020 Federal Employee of the Year Award, considered the “Oscars” of government service. Other finalists in the Service to America Awards this year are NIHers Ira Pastan, Nancy Sullivan, and the duo of John Tisdale and Griff Rodgers. A celebration was held on October 5.
October 2: President Donald Trump announces that he and First Lady Melania Trump have tested positive for COVID-19.
October 3: President Trump is admitted to Walter Reed Medical Center (Bethesda, Maryland), where he receives one dose of experimental monoclonal antibodies and is also treated with a several-day course of remdesivir and the steroid dexamethasone.
October 5: President Trump is released from Walter Reed and returns to the White House.
October 5: Harvey Alter is awarded the 2020 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for his contributions to the discovery of the hepatitis C virus that led to curative treatments and methods that keep the blood supply safe for transfusions.
October 5 Anthony Fauci is celebrated as the Service to America Medal 2020 Federal Employee of the Year. Ira Pastan is named the 2020 Winner of the Paul A. Volcker Career Achievement Award for his discovery of a new class of drugs that can successfully treat a rare form of leukemia and holds promise for other cancers.
October 6: NIH Rapid Acceleration of Diagnostics (RADx) initiative advances six new COVID-19 testing technologies. NIH announces the third set of COVID-19 testing technologies out of the RADx Tech program, led by the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering. These awards support additional novel testing approaches for new modes of sample collection, processing, and return of test results. This brings the total support of new early and late-stage COVID-19 testing technologies to $476.4 million and 22 companies.
October 8: The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases announces the start of a phase 3 clinical trial to test whether a treatment regimen of the antiviral remdesivir plus a highly concentrated solution of antibodies that neutralize SARS-CoV-2 virus is safe, tolerated, and effective in hospitalized patients. The trial is called the Inpatient Treatment with Anti-Coronavirus Immunoglobulin, or ITAC, trial, and the antibody solution being tested is anti-coronavirus hyperimmune intravenous immunoglobulin, or hIVIG. The antibodies in anti-coronavirus hIVIG come from plasma donated by people who have recovered from COVID-19. ITAC investigators hypothesize that giving people anti-coronavirus hIVIG at the onset of COVID-19 symptoms, before the body makes its own protective immune response, could augment the natural antibody response to SARS-CoV-2, thereby reducing the risk of more serious illness and death.
October 8: NCI announces the launch of the Serological Science Network for COVID-19 (SeroNet), which aims to quickly increase antibody testing capacity and improve understanding of immune response to COVID-19.
Oct 8: A final report confirming remdesivir benefits for COVID 19 is published in the New England Journal of Medicine (N Engl J Med NEJMoa2007764, 2020).
October 12: Johnson & Johnson announces that it is pausing its phase 3 vaccine trial due to an unexplained illness in one study participant (the trial resumes on October 23). Also paused this week is the ACTIV-3 trial testing the Eli Lilly monoclonal antibody (LY-CoV555) in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2. The AstraZeneca phase 3 clinical trial remains on hold in the United States but has resumed in other countries.
October 12: NIAID launches the phase 2 ACTIV-5 Big Effect Trial, which is designed to determine whether certain approved therapies or investigational drugs in late-stage clinical development show promise against COVID-19 and should advance to larger clinical trials. ACTIV-5 will enroll hospitalized patients in up to 40 U.S. sites and will initially separately test two monoclonal antibodies (risankizumab and lenzilumab) given in conjunction with remdesivir, now the standard of care, and compare them with placebo plus remdesivir.
October 16: NIH announces the start of the ACTIV-1 Immune Modulator trial, an adaptive phase 3 trial that aims to evaluate the safety and efficacy of three immune modulator drugs in hospitalized adults diagnosed with COVID-19. NCATS is coordinating the trial, which expects to enroll 2,100 hospitalized patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 in the United States and Latin America.
October 16: NIH is opening an exceptions process to allow federal employees who are teleworking under challenging circumstances to apply to voluntarily return to the physical workspace as part of Group C.
Oct 14–15: Dr. Sanjay Gupta joins NIH and CDC officials as well as Fortune 500 and International C-Level business executives presenting at the Everbridge COVID-19 Road to Recovery (R2R) Virtual Summit.
Week of October 19: Moderna announces that it has reached its phase 3 vaccine trial enrollment goal of 30,000 participants, with 42% of those from high-risk groups. NIH, Operation Warp Speed, and the Surgeon General worked intensively with the company to increase representation of minority groups, with a total of 11,000 people from communities of color, or 37% of the trial population. The company indicates it won’t be ready to file for an Emergency Use Authorization until late November at the earliest. NIH Director Francis Collins congratulates Moderna and the teams of people at NIAID, NHLBI, NIMHD, and the Vaccine Research Center who have worked tirelessly to make this enrollment happen.
October 23: Maryland’s Montgomery County Chamber of Commerce (MCCC) announces the 2020 Business Award Winners and Sponsors. The 2020 Visionary of the Year Award goes to NIH. This award is typically presented during the MCCC Annual Dinner, but due to the global pandemic, the MCCC board of directors and the Business Awards Selection Committee made the decision to add this award to the Business Awards program. This award recognizes an individual or an organization for its innovation and tremendous contributions to the county and beyond. During the live broadcast, NIH Director Francis S. Collins and NIAID Director Anthony S. Fauci will accept the award on behalf of NIH. The award ceremony will be broadcast on social media at 4:00 p.m., Eastern Daylight Savings Time, on October 29.
October 28: Cell paper reports that NHLBI researchers discovered a biological pathway that the novel coronavirus appears to use to hijack and exit cells as it spreads through the body. (journal pre-proof Cell, 2020; doi:10.1016/ j.cell.2020.10.039)
October 29 and 30: The NIH/FDA COVID-19 Research Workshop, held virtually, highlights the breadth of work on COVID-19 in talks and flash talks/posters from the NIH and FDA research community.
October 31: In a virtual celebration, NIH marks the 80th anniversary of President Franklin Roosevelt’s October 31, 1940 dedication of the NIH campus.
This page was last updated on Monday, March 21, 2022
