Commonly used antibiotic shows promise for combating Zika infections
NIH preclinical study suggests FDA-approved tetracycline-based antibiotics may slow infection and reduce neurological problems
In 2015, hundreds of children were born with brain deformities resulting from a global outbreak of Zika virus infections. Recently, National Institutes of Health researchers used a variety of advanced drug screening techniques to test out more than 10,000 compounds in search of a cure. To their surprise, they found that the widely used antibiotic methacycline was effective at preventing brain infections and reducing neurological problems associated with the virus in mice. In addition, they found that drugs originally designed to combat Alzheimer’s disease and inflammation may also help fight infections.
“Around the world, the Zika outbreak produced devastating, long-term neurological problems for many children and their families. Although the infections are down, the threat remains,” said Avindra Nath, M.D., senior investigator at the NIH’s National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) and a senior author of the study published in PNAS. “We hope these promising results are a good first step to preparing the world for combating the next potential outbreak.”
The study was a collaboration between scientists on Dr. Nath’s team and researchers in laboratories led by Anton Simeonov, Ph.D., scientific director at the NIH’s National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS) and Radhakrishnan Padmanabhan, Ph.D., Professor of Microbiology & Immunology, Georgetown University Medical Center, Washington, D.C.
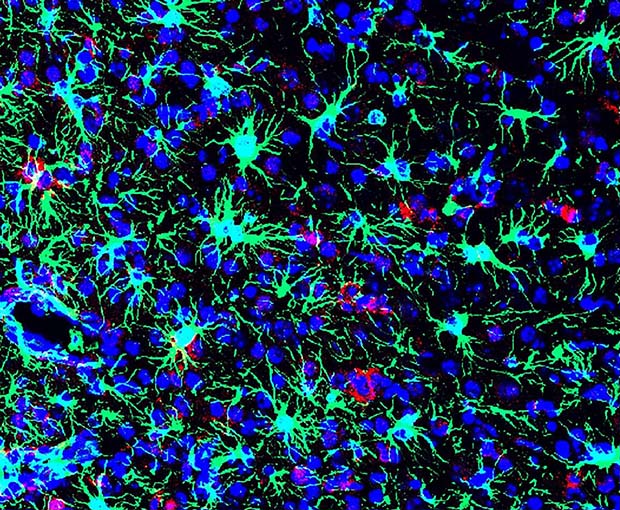
NIH scientists found that the commonly used antibiotic methacycline may be effective at combating the neurological problems caused by Zika virus infections. This is a picture of a Zika-infected mouse brain from the study. Image credit: Nath lab, NIH/NINDS
This page was last updated on Friday, January 21, 2022