Autoimmunity may be rising in the United States
Autoimmunity, a condition in which the body’s immune system reacts with components of its own cells, appears to be increasing in the United States, according to scientists at the National Institutes of Health and their collaborators.
In a study published April 8 in Arthritis and Rheumatology, the researchers found that the prevalence of antinuclear antibodies (ANA), the most common biomarker of autoimmunity, was significantly increasing in the United States overall and particularly in certain groups. These groups include males, non-Hispanic whites, adults 50 years and older, and adolescents. The study is the first to evaluate ANA changes over time in a representative sampling of the U.S. population.
"The reasons for the increases in ANA are not clear, but they are concerning and may suggest a possible increase in future autoimmune disease," said corresponding and senior author Frederick Miller, M.D., Ph.D., deputy chief of the Clinical Research Branch at the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS), part of NIH. "These findings could help us understand more about the causes of these immune abnormalities and possibly learn what drives development of autoimmune diseases and how to prevent them."
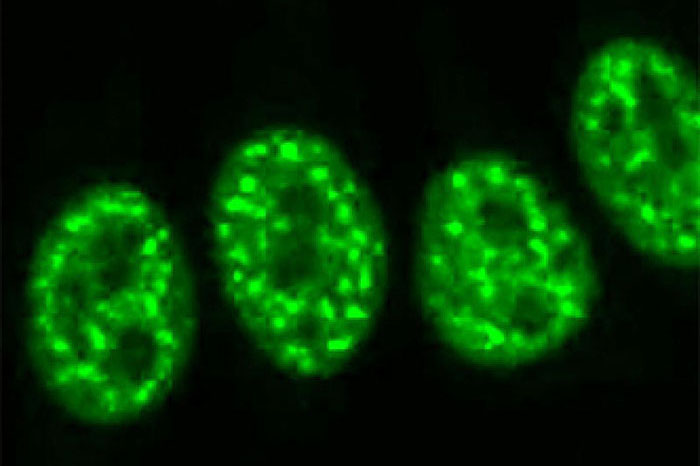
Immunofluorescent staining of human cells shows ANA as bright dots. Image courtesy of Edward Chan, Ph.D., University of Florida
This page was last updated on Friday, January 21, 2022