
Research Topics
Research in the Vector Biology Section explores the biochemical and pharmacological diversity found in the salivary glands of blood feeding insects and ticks. Molecular, biochemical, and pharmacological approaches are used in our research. Recently, we have used vector salivary gland transcriptome analysis to discover new and interesting compounds and for that reason have developed tools for bioinformatic analysis.
Ixolaris, a novel TFPI moleculeIn each of the major areas of research, we seek discoveries that improve our basic knowledge of the evolution of the blood feeding behavior, at the same time generating novel compounds that can be of pharmacological use or developed as vaccine targets. Inquiries about predoctoral and postdoctoral fellowships as well as Ph.D. studentships in the National Institutes of Health Graduate Partnership Program are welcome.
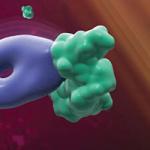
The figure shows the structure of Ixolaris, an anti-clotting protein derived from the tickIxodes scapularis (also pictured). This protein has anti-clotting and anti-metastatic properties.
Biography
Dr. Ribeiro received his M.D. from the State University of Rio de Janeiro and a Ph.D. from the Biophysics Institute of the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro. He was an assistant and associate professor at the Harvard School of Public Health and professor at the department of entomology in the University of Arizona before joining NIAID in 1996. His work focuses on the role of vector saliva in blood feeding by arthropods, where a great diversity of pharmacologically active compounds and new targets for vaccination against vector-borne diseases have been uncovered. Dr. Ribeiro has served for many years in the Tropical Diseases Research Program of the World Health Organization and as editor and reviewer for several journals.
Selected Publications
- Kim IH, Castillo JC, Aryan A, Martin-Martin I, Nouzova M, Noriega FG, Barletta ABF, Calvo E, Adelman ZN, Ribeiro JMC, Andersen JF. A mosquito juvenile hormone binding protein (mJHBP) regulates the activation of innate immune defenses and hemocyte development. PLoS Pathog. 2020;16(1):e1008288.
- Lu S, Andersen JF, Bosio CF, Hinnebusch BJ, Ribeiro JM. Acid phosphatase-like proteins, a biogenic amine and leukotriene-binding salivary protein family from the flea Xenopsylla cheopis. Commun Biol. 2023;6(1):1280.
- Andersen JF, Lei H, Strayer EC, Kanai T, Pham V, Pan XZ, Alvarenga PH, Gerber GF, Asojo OA, Francischetti IMB, Brodsky RA, Valenzuela JG, Ribeiro JMC. A bispecific inhibitor of complement and coagulation blocks activation in complementopathy models via a novel mechanism. Blood. 2023;141(25):3109-3121.
- Andersen JF, Lei H, Strayer EC, Pham V, Ribeiro JMC. Mechanism of complement inhibition by a mosquito protein revealed through cryo-EM. Commun Biol. 2024;7(1):649.
- Alvarenga PH, Alves E Silva TL, Suzuki M, Nardone G, Cecilio P, Vega-Rodriguez J, Ribeiro JMC, Andersen JF. Comprehensive Proteomics Analysis of the Hemolymph Composition of Sugar-Fed Aedes aegypti Female and Male Mosquitoes. J Proteome Res. 2024;23(4):1471-1487.
Related Scientific Focus Areas

Molecular Biology and Biochemistry
View additional Principal Investigators in Molecular Biology and Biochemistry


Microbiology and Infectious Diseases
View additional Principal Investigators in Microbiology and Infectious Diseases

This page was last updated on Monday, September 30, 2024