Novel technique reduces obstruction risk in heart valve replacement
The transcatheter approach increases treatment options for high-risk patients
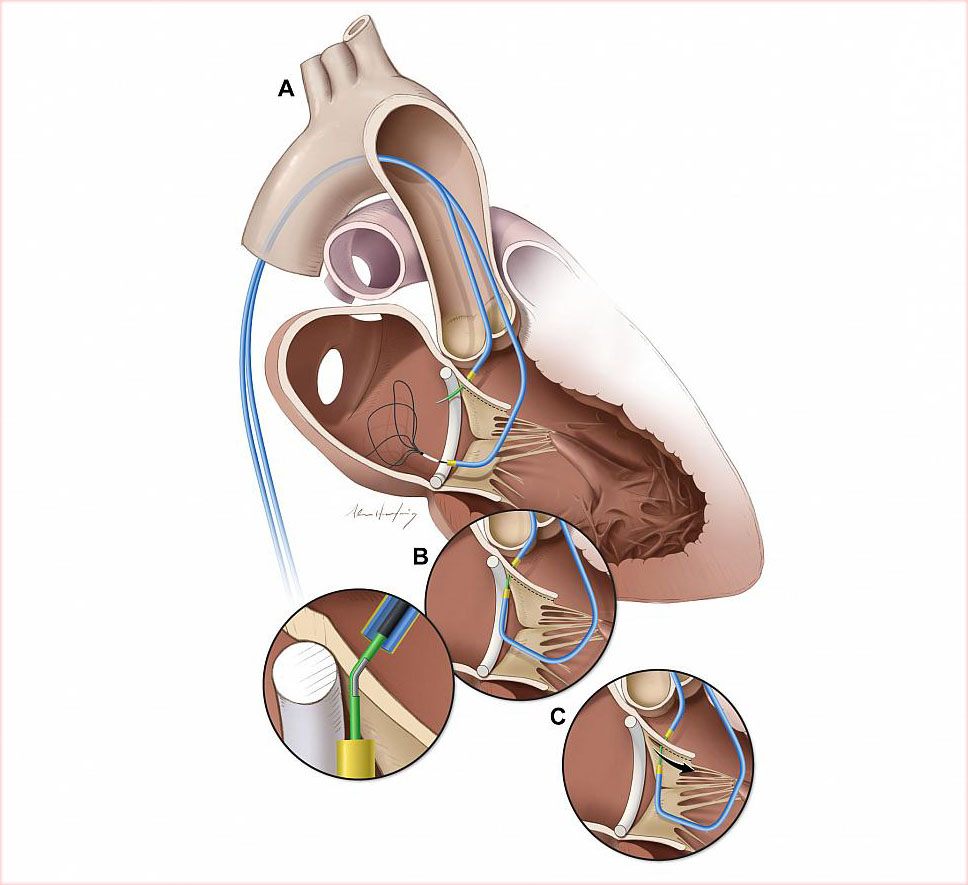
Researchers at the National, Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), part of the National Institutes of Health, have developed a novel technique that prevents the obstruction of blood flow, a common fatal complication of transcatheter mitral valve replacement (TMVR). The new method, called LAMPOON, may increase treatment options for high-risk patients previously ineligible for heart valve procedures. The Journal of the American College of Cardiology published the findings online on May 20.
TMVR is used to treat mitral valve stenosis, a narrowing of the valve that restricts blood flow into the main pumping chamber of the heart. It also treats regurgitation, which occurs when the valve leaks and causes blood to flow back through the valve. Untreated, these conditions can cause pulmonary hypertension, heart enlargement, atrial fibrillation, blood clots, and heart failure.
For elderly or frail patients, TMVR offers a less invasive alternative to open heart surgery. During TMVR, doctors replace the mitral valve by delivering an artificial valve through a long, thin, flexible tube, called a catheter, through blood vessels and into the heart. But in more than 50 percent of patients, the heart’s anatomy gets in the way. The heart leaflet is pushed back and blocks blood flow. This is known as left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) obstruction, a common and the most life-threatening complication of TMVR.
“These patients have a failing mitral valve, are not able to undergo open heart surgery, and are now rejected as candidates for TMVR because of the very high risk of left ventricular outflow tract obstruction,” said study author Jaffar M. Khan, M.D., clinician at NHLBI.
This page was last updated on Friday, January 21, 2022