Microbleeds may worsen outcome after head injury
NIH study examines effects of blood vessel damage following brain injury
Using advanced imaging, researchers have uncovered new information regarding traumatic microbleeds, which appear as small, dark lesions on MRI scans after head injury but are typically too small to be detected on CT scans. The findings published in Brain suggest that traumatic microbleeds are a form of injury to brain blood vessels and may predict worse outcomes. The study was conducted in part by scientists at the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), part of the National Institutes of Health.
“Traumatic microbleeds may represent injury to blood vessels that occur following even minor head injury,” said Lawrence Latour, Ph.D., NINDS researcher and senior author of the study. “While we know that damage to brain cells can be devastating, the exact impact of this vascular injury following head trauma is uncertain and requires further study.”
This study, which involved researchers from Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory in New York and the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences in Bethesda, Maryland, included 439 adults who experienced head injury and were treated in the emergency department. The subjects underwent MRI scans within 48 hours of injury, and again during four subsequent visits. Participants also completed behavioral and outcome questionnaires.
The results showed that 31% of all study participants had evidence of microbleeds on their brain scans. More than half (58%) of participants with severe head injury showed microbleeds as did 27% of mild cases. The microbleeds appeared as either linear streaks or dotted, also referred to as punctate, lesions. The majority of patients who exhibited microbleeds had both types. The findings also revealed that the frontal lobes were the brain region most likely to show microbleeds.
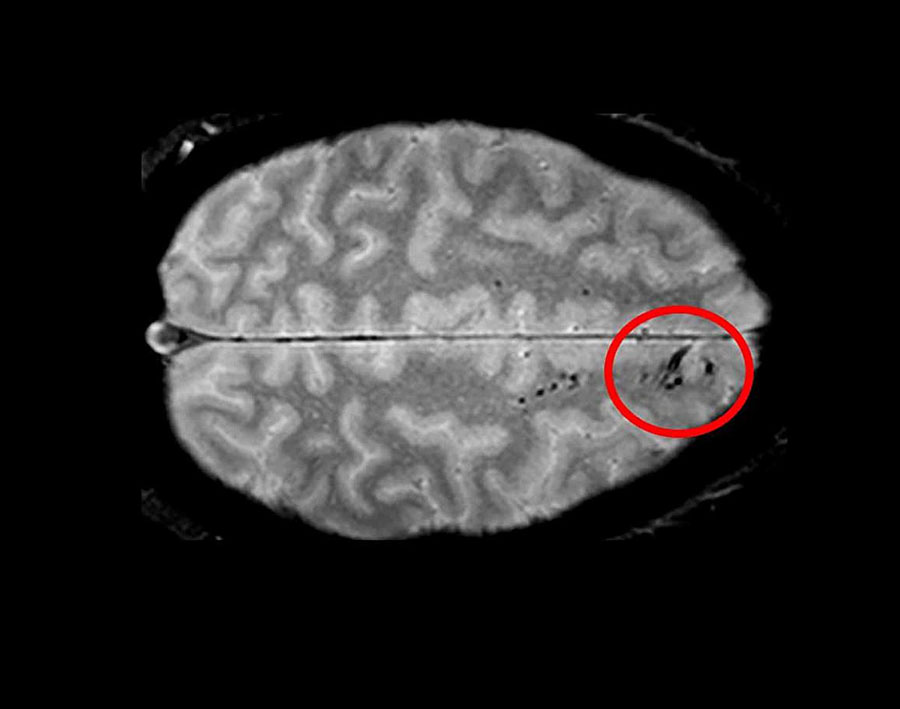
Traumatic microbleeds appear as dark lesions on MRI scans and suggest damage to brain blood vessels after head injury.
This page was last updated on Friday, January 21, 2022