IRP scientists use human cerebral organoid to test drug for deadly brain disease
Approximately two years after establishing a human cerebral organoid system to study Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD), National Institutes of Health researchers have further developed the model to screen drugs for potential CJD treatment. The scientists, from NIH’s National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), describe their work in Scientific Reports.
Human cerebral organoids are small balls of human brain cells ranging in size from a poppy seed to a pea; scientists use human skin cells to create them. CJD, a fatal neurodegenerative brain disease of humans caused by infectious prion proteins, affects about 1 in 1 million people each year. It can arise spontaneously, result from a hereditary mutation within the prion gene, or arise due to infection, for example, from eating contaminated meat products. A notable example of this occurred in the United Kingdom in the mid-1990s following an outbreak of bovine spongiform encephalopathy in cattle. There are no preventive or therapeutic treatments for CJD.
The lack of a completely human CJD model has been a considerable barrier hindering the discovery of potential therapies. Studies in mice have failed to identify treatments that were then effective when tried in patients. The human cerebral organoid CJD model holds promise that this barrier can be eliminated. Cerebral organoids have organization, structure, and electrical signaling systems similar to human brain tissue. Because they can survive in a controlled environment for months to years, cerebral organoids also are ideal for studying nervous system diseases over lengthy periods of time. Cerebral organoids have been used as models to study Zika virus infection, Alzheimer’s disease, and Down syndrome.
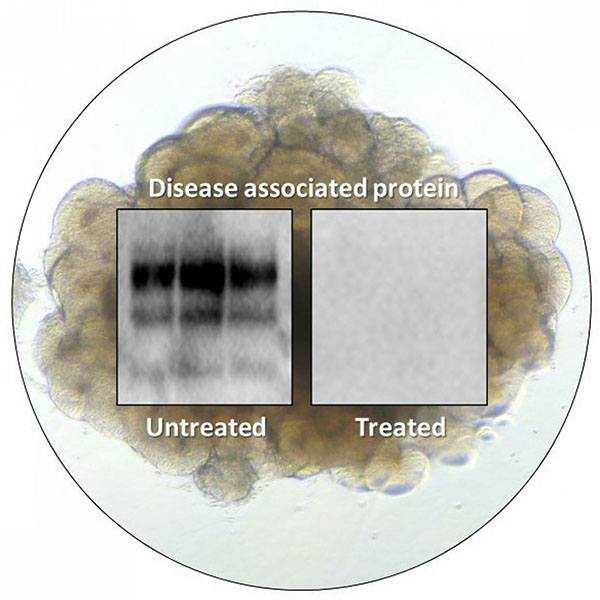
A cerebral organoid shown overlaid with test results from prion infected organoids that were left untreated or treated with PPS. The results show that treatment reduces disease-associated protein.
This page was last updated on Friday, January 21, 2022