IRP scientists create 3D structure of 1918 influenza virus-like particles
Details could advance vaccine development for several human diseases
Virus-like particles (VLPs) are protein-based structures that mimic viruses and bind to antibodies. Because VLPs are not infectious, they show considerable promise as vaccine platforms for many viral diseases, including influenza. Realizing that fine details about influenza VLPs were scant, a team of researchers who specialize in visualizing molecular structures developed a 3D model based on the 1918 H1 pandemic influenza virus. They say their research, which appears online in Scientific Reports, could benefit VLP vaccine projects, targeting a range of viruses from HIV to Ebola and SARS coronavirus. The research was conducted by scientists at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health.
Other researchers had produced VLPs for 1918 H1 influenza that successfully protected animals from different influenza viruses. The NIAID group prepared hundreds of such VLP samples and analyzed their structure with a technique called cryo-electron microscopy, which quick-freezes samples with glass-like clarity. They then sliced through those VLP 3D structures—like slicing through a loaf of bread—to analyze their internal structure, using computers to document the size and placement of key molecules. After averaging all their data, the group then created a 3D 1918 influenza VLP model.
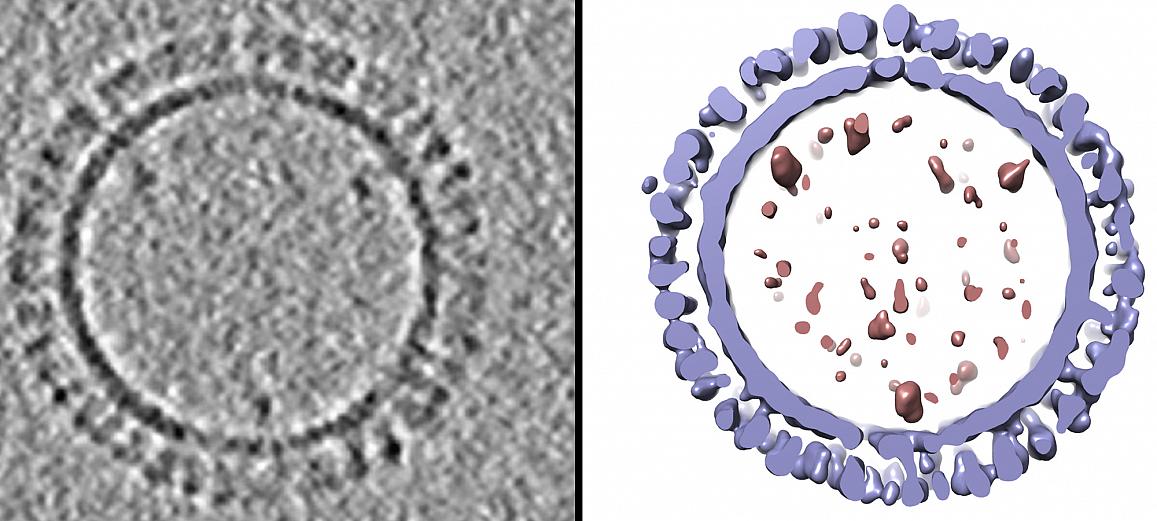
On the left is a 1918 H1 influenza virus-like particle (VLP) as seen by cryo-electron microscopy. On the right is the same VLP rendered in 3D with structural components computationally segmented and colored; hemagglutinin and membrane are light blue and internal components (molecular cargo) are red.
This page was last updated on Friday, January 21, 2022