IRP researchers discover tooth-enamel protein in eyes with dry AMD
Finding may lead to novel therapeutic target for blinding disease
A protein that normally deposits mineralized calcium in tooth enamel may also be responsible for calcium deposits in the back of the eye in people with dry age-related macular degeneration (AMD), according to a study from researchers at the National Eye Institute (NEI). This protein, amelotin, may turn out to be a therapeutic target for the blinding disease. The findings were published in the journal Translational Research. NEI is part of the National Institutes of Health.
“Using a simple cell culture model of retinal pigment epithelial cells, we were able to show that amelotin gets turned on by a certain kind of stress and causes formation of a particular kind of calcium deposit also seen in bones and teeth. When we looked in human donor eyes with dry AMD, we saw the same thing,” said Graeme Wistow, Ph.D., chief of the NEI Section on Molecular Structure and Functional Genomics, and senior author of the study.
There are two forms of AMD — wet and dry. While there are treatments that can slow the progression of wet AMD, there are currently no treatments for dry AMD, also called geographic atrophy. In dry AMD, deposits of cholesterol, lipids, proteins, and minerals accumulate at the back of the eye. Some of these deposits are called soft drusen and have a specific composition, different from deposits found in wet AMD. Drusen form under the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), a layer of cells that transports nutrients from the blood vessels below to support the light-sensing photoreceptors of the retina above them. As the drusen develop, the RPE and eventually the photoreceptors die, leading to blindness. The photoreceptors cannot grow back, so the blindness is permanent.
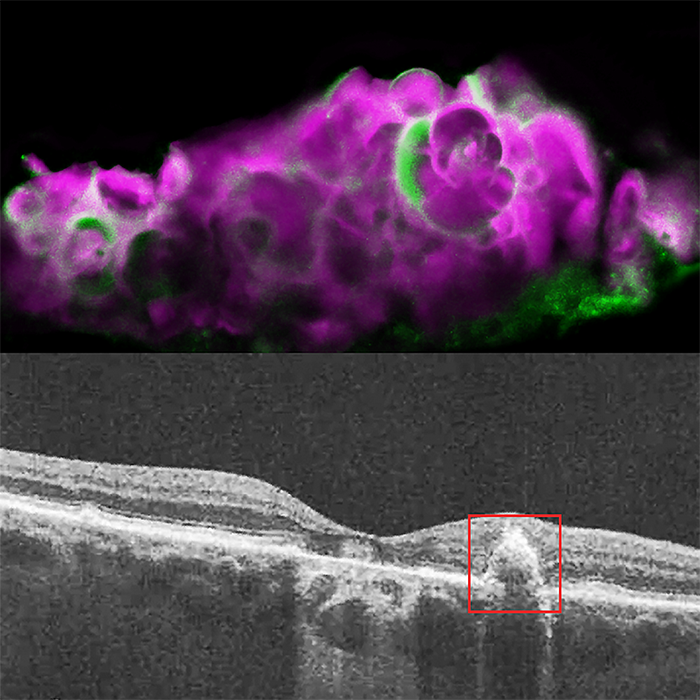
Top: HAP spherules (pink) and amelotin protein (green) in soft drusen from eye with dry AMD. Bottom: OCT image of eye with dry AMD, showing soft drusen beneath the retinal pigment epithelium.
This page was last updated on Friday, January 21, 2022