IRP clinical trial leads to atezolizumab approval for advanced alveolar soft part sarcoma
A clinical trial led by the National Cancer Institute (NCI), part of the National Institutes of Health, has resulted in the first approval of a treatment for advanced alveolar soft part sarcoma (ASPS). The immunotherapy drug atezolizumab (Tecentriq) was recently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of adults and children 2 years and older with ASPS that has spread to other parts of the body or cannot be removed by surgery.
ASPS is an extremely rare cancer that affects mostly adolescents and young adults. The approval was based on data from a non-randomized phase 2 trial funded by NCI and led by Dr. Alice Chen, M.D., of the Developmental Therapeutics Clinic in NCI’s Division of Cancer Treatment and Diagnosis (DCTD). Genentech, a member of the Roche Group and the manufacturer of atezolizumab, provided the drug to NCI through a cooperative research and development agreement. The results of the study are being prepared for publication.
“Forty percent of the patients were treated at the NIH Clinical Center in Bethesda," said James H. Doroshow, M.D., director of DCTD. “Our ability to bring patients in from all over the world was a key factor in the ability to do the study.”
“This approval will make a huge impact in terms of a rare disease that has been particularly challenging to treat,” Dr. Chen noted.
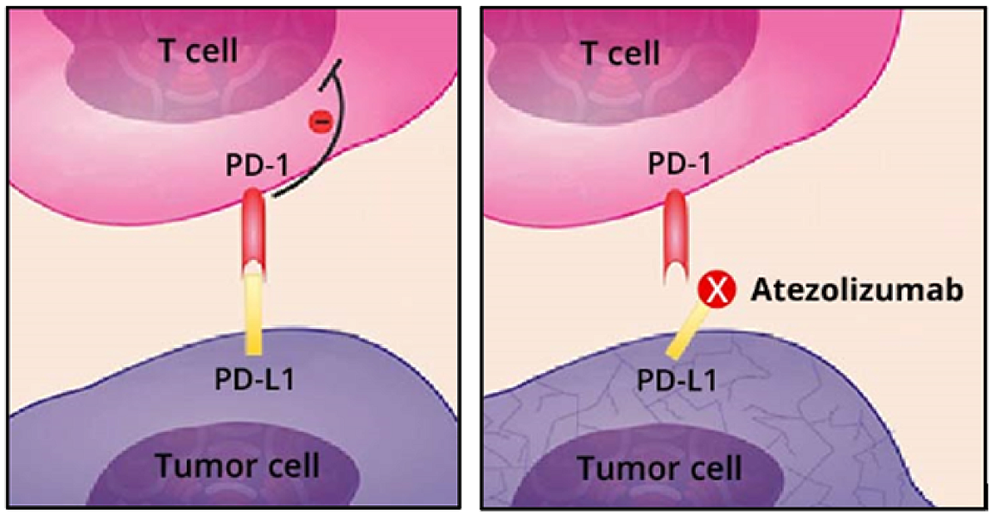
Left frame: Normally, tumor cells (purple) evade the immune system’s T cells (pink) by expressing a checkpoint protein known as PD-L1. Right frame: Atezolizumab (Tecentriq) binds to PD-L1 and blocks it from binding to another checkpoint protein, PD-1. This helps T cells regain their ability to kill tumor cells.
This page was last updated on Wednesday, December 28, 2022