Drug shows promise for slowing progression of rare, painful genetic disease
NIH-supported clinical trial could lead to first effective treatment for ACDC disease
A drug used to treat certain bone diseases shows promise for slowing the progression of a rare, painful genetic condition that causes excessive calcium buildup in the arteries, known as arterial calcification due to deficiency of CD73 (ACDC). These results are from a first-in-human clinical trial supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), part of the National Institutes of Health. The study, published in the journal Vascular Medicine, could lead to the first effective treatment for the rare disease.
ACDC, which has no known cure, often targets the arteries of the legs and can make walking painful and difficult. It can also affect the joints of the hands, causing pain and deformities. In severe cases, the condition can lead to potential limb loss. Symptoms of the disease often begin in the late teens and 20s. An extremely rare disease, it is believed to affect only about 20 people worldwide and has an estimated prevalence of less than 1 in 1 million. Previous studies have identified the gene for ACDC disease and the biochemical mechanism behind it. More recent studies by the NHLBI research team identified an existing drug, called etidronate, as a potential treatment for ACDC based on disease models in animals and human cells.
In the study, researchers evaluated the safety and effectiveness of etidronate in treating calcification of the arteries and impaired blood flow in the legs of seven people (four women and three men) with ACDC disease. Although few, they collectively represent about one-third of all the known cases in the world. Treatment consisted of taking the oral drug daily for 14 days every three months over a three-year period. The researchers measured calcium deposits using CT scans and tested blood flow using the ankle brachial index, a non-invasive tool, both at the start of the study and as a yearly follow-up after treatment.
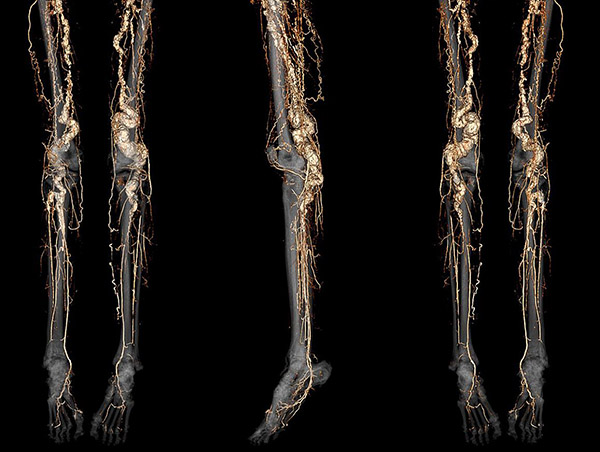
A CT angiography scan of a person with ACDC disease showing abnormal calcification of the blood vessels in the legs and feet.
This page was last updated on Wednesday, April 3, 2024