Astrocytes regulate signal speeds of neurons
NIH findings in rodents suggest astrocytes play important role in how the brain processes information.
The transmission speed of neurons fluctuates in the brain to achieve an optimal flow of information required for day-to-day activities, according to a National Institutes of Health study. The results, appearing in PNAS, suggest that brain cells called astrocytes alter the transmission speed of neurons by changing the thickness of myelin, an insulation material, and the width of gaps in myelin called nodes of Ranvier, which amplify signals.
“Scientists used to think that myelin could not be thinned except when destroyed in demyelinating diseases, such as multiple sclerosis,” said R. Douglas Fields, Ph.D., senior author and chief of the Section on Nervous System Development and Plasticity at NIH’s Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD). “Our study suggests that under normal conditions, the myelin sheath and structure of the nodes of Ranvier are dynamic, even in adults.”
The brain is composed of neurons, which have extensions called axons that can stretch for long distances. Axons are wrapped by layers of myelin, which serve as insulation to increase the speed of signals relayed by neurons. Gaps between segments of myelin are called nodes of Ranvier, and the number and width of these gaps can also regulate transmission speed.
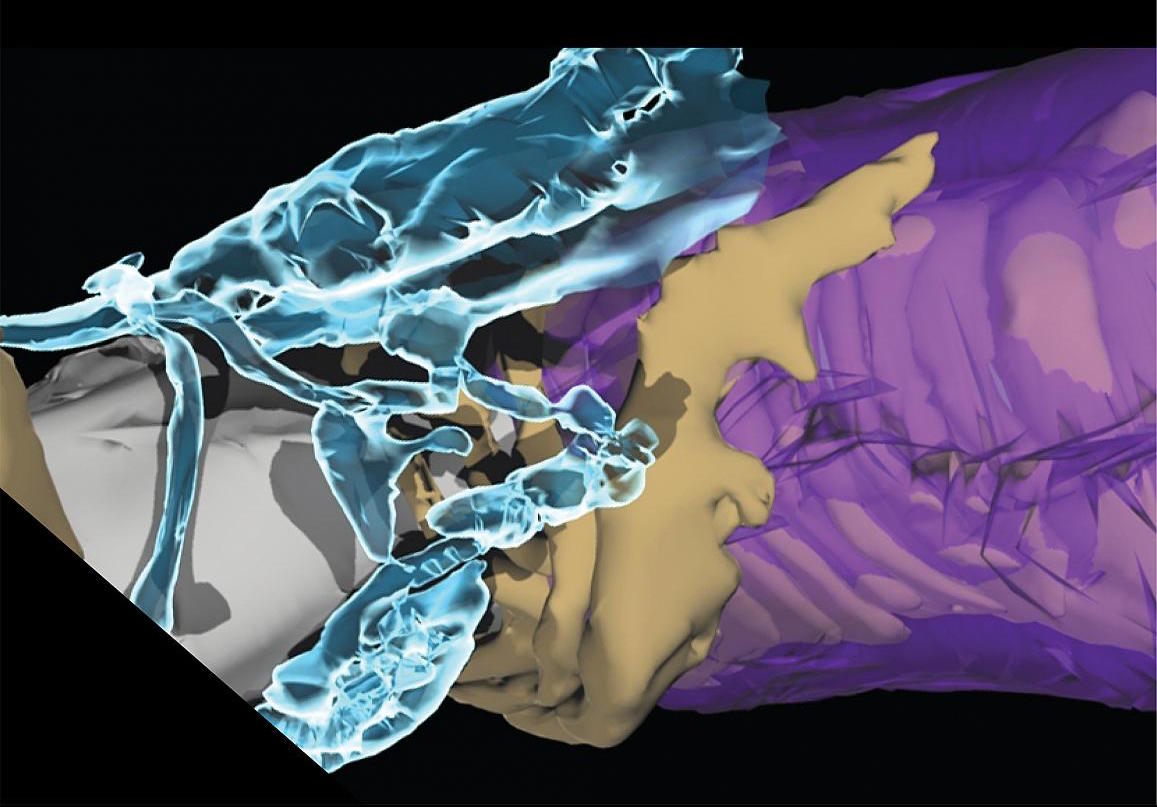
3D reconstruction of electron microscopy images of a perinodal astrocyte (blue), node of Ranvier (gray), compact myelin (purple), and layers of myelin detaching from the axon (tan).
This page was last updated on Friday, January 21, 2022