Researchers restore sight in mice by turning skin cells into light-sensing eye cells
NIH-funded study offers new path to modeling eye disease, advancing therapies
Researchers have discovered a technique for directly reprogramming skin cells into light-sensing rod photoreceptors used for vision. The lab-made rods enabled blind mice to detect light after the cells were transplanted into the animals’ eyes. The work, funded by the National Eye Institute (NEI), published April 15 in Nature. The NEI is part of the National Institutes of Health.
Up until now, researchers have replaced dying photoreceptors in animal models by creating stem cells from skin or blood cells, programming those stem cells to become photoreceptors, which are then transplanted into the back of the eye. In the new study, scientists show that it is possible to skip the stem-cell intermediary step and directly reprogram skins cells into photoreceptors for transplantation into the retina.
“This is the first study to show that direct, chemical reprogramming can produce retinal-like cells, which gives us a new and faster strategy for developing therapies for age-related macular degeneration and other retinal disorders caused by the loss of photoreceptors,” said Anand Swaroop, Ph.D., senior investigator in the NEI Neurobiology, Neurodegeneration, and Repair Laboratory, which characterized the reprogrammed rod photoreceptor cells by gene expression analysis.
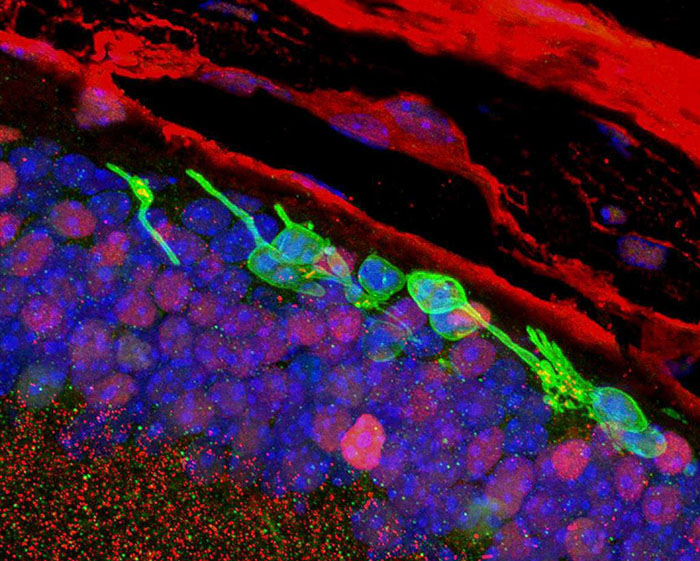
Three months after transplantation, immunofluorescence studies confirmed the survival of the chemically induced photoreceptor-like cells (green). They also show integration of the cells into the layers of the mouse retina.
This page was last updated on Friday, January 21, 2022