NIDA researchers confirm important brain reward pathway
NIH study in rodents identifies a pathway that starts with glutamate and ends with activation of dopamine reward system
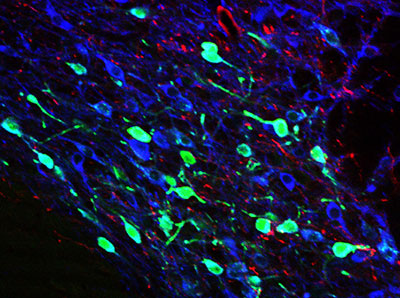
Details of the role of glutamate, the brain’s excitatory chemical, in a drug reward pathway have been identified for the first time. This discovery in rodents — published today in Nature Communications — shows that stimulation of glutamate neurons in a specific brain region (the dorsal raphe nucleus) leads to activation of dopamine-containing neurons in the brain’s reward circuit (dopamine reward system).
This page was last updated on Friday, January 21, 2022