IRP scientists study salmonella swimming behavior as clues to infection
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium bacteria (S. Typhimurium) commonly cause human gastroenteritis, inflammation of the lining of the intestines. The bacteria live inside the gut and can infect the epithelial cells that line its surface. Many studies have shown that Salmonella use a “run-and-tumble” method of short swimming periods (runs) punctuated by tumbles when they randomly change direction, but how they move within the gut is not well understood.
National Institutes of Health scientists and their colleagues believe they have identified a S. Typhimurium protein, McpC (Methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein C), that allows the bacteria to swim straight when they are ready to infect cells. This new study, published in Nature Communications, describes S. Typhimurium movement and shows that McpC is required for the bacteria to invade surface epithelial cells in the gut.
The study authors suggest that McpC is a potential target for developing new antibacterial treatments to hinder the ability of S. Typhimurium to infect intestinal epithelial cells and colonize the gut. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases scientists at Rocky Mountain Laboratories in Hamilton, Montana, led the study. Collaborators included groups from the University of Texas A&M campuses in College Station and Kingsville.
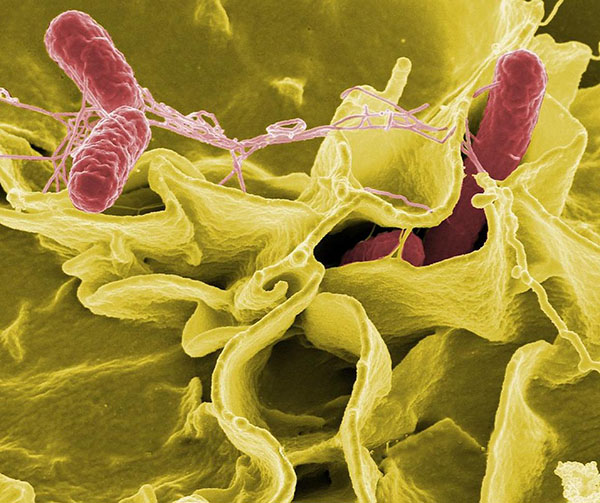
Salmonella bacteria (pink), a common cause of foodborne disease, invade a human epithelial cell (yellow).
This page was last updated on Friday, January 21, 2022